and the distribution of digital products.
DeCharge Network: Decentralizing EV Charging
- DeCharge enables individuals and small businesses to deploy EV chargers and participate in a token-incentivized network, lowering the cost and complexity of expanding public charging infrastructure, especially in under-served regions.
- Several ecosystem integrations have gone live since late 2024, including DePHY’s Open Source Energy Module for energy optimization, GEODNET’s GNSS nodes for precise positioning, and Linera’s microchain support for scalable offchain data processing.
- DeCharge’s token is yet to launch, but participation programs like Genesis Points and ZK Points are underway. These systems are designed to bootstrap early contributors ahead of the public token rollout and Energy Marketplace launch in 2025.
- Following a $2.5 million seed round led by Lemniscap in March 2025, DeCharge is focused on global network expansion, next-generation hardware with integrated storage, and the development of decentralized energy coordination tools.
Electric vehicle (EV) adoption continues to rise globally, but charging infrastructure hasn’t kept pace, especially in underserved markets with unreliable grids or weak economic incentives.
DeCharge offers a decentralized alternative: a community-powered EV charging network that lowers deployment barriers through distributed ownership and token-based incentives. Instead of relying on centralized operators or government-led infrastructure initiatives, DeCharge enables individuals and small businesses to deploy chargers; including the 3.3 kW Mini, 7 kW DeCharge Beast, and 60 kW, 120 kW, 240 kW, and 400 kW Titan models, and earn from network usage. The system is coordinated on Solana, with offchain components handling data, messaging, and energy optimization.
BackgroundDeCharge was founded in 2024 by Mohan Kuldeep Ponnada, Dr. Prakash Kamaraj, and Rama Krisha, who have experience in wireless energy systems, decentralized networks, and hardware deployments. The project began with early research into autonomous charging solutions for drones and small-scale robotics, ultimately leading to a prototype that placed second in Solana’s Renaissance Hackathon (DePIN track) in 2023. These early efforts shaped the team’s approach to combining real-world hardware with blockchain-based incentives.
By mid-2024, the team pivoted to a broader EV infrastructure opportunity, particularly in underserved markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa. DeCharge’s model leverages blockchain to manage charger availability, reward participants, and coordinate data, allowing for lower deployment costs and faster geographic expansion compared to centralized networks.
The project gained early validation from Solana’s developer ecosystem, including support from Superteam in India. It also recorded notable traction across its initial pilots, surpassing one million cumulative charging minutes by December 2024, and won the DePIN category at India Blockchain Week’s demo day. In March 2025, DeCharge raised a $2.5 million seed round led by Lemniscap, with participation from Colosseum, Daedalus, and other early-stage investors, to support hardware manufacturing, global expansion, and software development.
TechnologyNetwork DesignDeCharge infrastructure combines distributed hardware and software systems, coordinated through a blockchain-based protocol. The network supports three core charger types deployable by individuals or businesses:
- Mini (3.3 kW): The most widely used node in DeCharge’s rollout model, designed for small-scale, low-power residential, and neighborhood deployments.
- Beast (7 kW): An AC (Alternating Current) charger suitable for homes, apartments, and small businesses. It is OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) compliant, internet-connected, and supports integration with standard EV hardware. A second-generation Beast is in development, featuring an 11 kWh battery for backup power and off-grid operation.
- Titan-60, 120, 240 & 400 (60–400 kW): A high-capacity DC (Direct Current) fast charger intended for highways, pit stops, and high-traffic commercial areas. These units are designed for fast turnaround and can support multiple vehicles at scale.
All chargers feed data to DeCharge’s coordination layer and support revenue-sharing incentives based on usage, uptime, and geographic demand.
Source: DeCharge Network
Coordination Layer & SoftwareThe network is coordinated on Solana, chosen for its low transaction costs and high throughput. To manage high-frequency data such as session telemetry and device heartbeat signals, DeCharge integrates with microchain protocol (e.g., Linera) to offload processing and ensure low-latency synchronization between physical devices and the onchain coordination layer. The system also employs H3 spatial indexing to map regional demand and optimize hardware deployment, prioritizing areas with low public charging coverage.
Planned AI-enhanced features include:
- Dynamic pricing, adjusting fees based on time-of-use or grid load;
- Smart routing, which recommends available nearby stations based on charger status and queue times.
Users can access charging via the DeCharge mobile app, which supports station discovery, reservations, and fiat payments. Token incentives are used to encourage usage, allowing drivers to earn rewards that can offset charging costs.
On the infrastructure side, DeCharge validates charger uptime and energy delivery through a verifiable service model (akin to “proof-of-charge”), where devices regularly submit performance metrics to qualify for rewards.
Additionally, each deployed Beast charger includes an embedded Open Source Energy Module (OSEM) from the DePHY Network, enabling it to function as a node in DePHY’s separate decentralized energy optimization system. This dual integration allows hosts to earn rewards from both networks while contributing to broader energy intelligence use cases such as load balancing and battery management.
DeCharge TokenWhile the DeCharge network currently supports fiat-based payments and USDT on Solana, its long-term incentive structure centers around a forthcoming native token (ticker unannounced as of April 2025). The token is designed to coordinate network participation and support decentralized infrastructure ownership and operations.
- Incentives & Rewards: The token will primarily serve as an incentive mechanism to bootstrap activity across the network. Charger hosts are expected to earn rewards based on verified uptime, energy dispensed, and charger placement in high-priority areas. Similarly, drivers may receive token-based rebates for completed charging sessions. These rewards are designed to accelerate adoption by compensating both infrastructure providers and users during the early growth phase.
- Medium of Exchange: The token is expected to serve as the medium of exchange within the planned DeCharge Energy Marketplace, a platform for peer-to-peer services such as energy credit transfers, resale of prepaid sessions, and grid participation. The token utility may also include discounted charging fees, reservation priority, and other in-app benefits
- Governance Participation: Over time, token holders may gain governance rights over key protocol decisions, such as reward structure adjustments, treasury allocation, and deployment strategies. While not yet implemented, this approach would align DeCharge with Web3 principles of community-led infrastructure governance.
As of April 2025, the token remains in a pre-launch phase. The protocol has not disclosed the final supply, emission schedule, or distribution mechanics. However, seasonal point systems like Genesis Points and ZK Points that reward early contributors may be correlated with future token allocations. These programs are intended to establish baseline demand and activity before a broader token release.
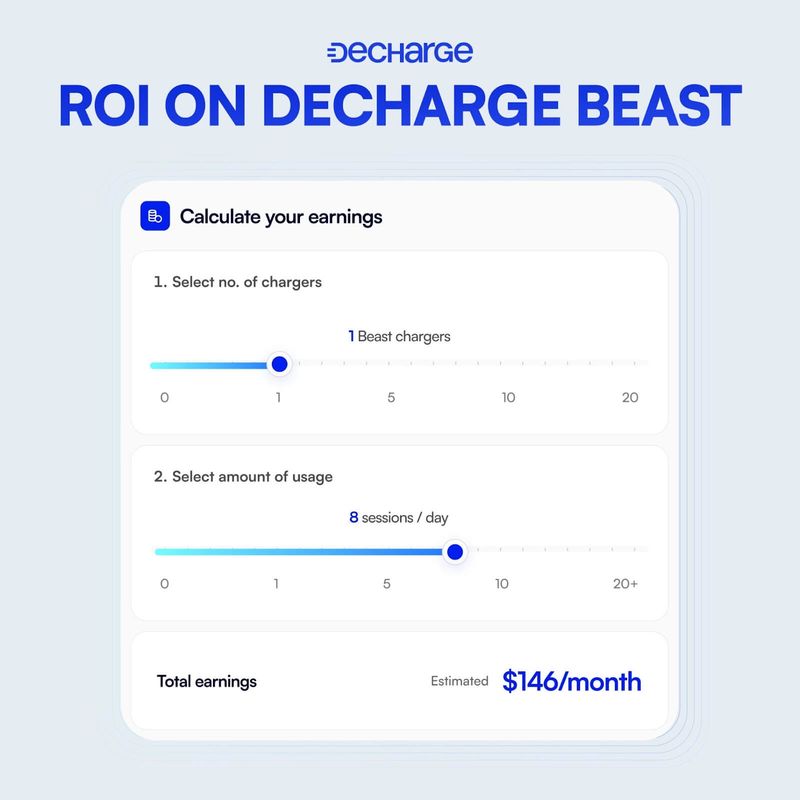
Consumer ROI AnalysisDeCharge’s infrastructure model enables individuals and small businesses to deploy and operate EV chargers, offering access to a revenue stream traditionally limited to centralized, capital-intensive operators. While DeCharge does not reduce deployment costs for individual hosts, it distributes infrastructure ownership and allows participants to earn directly from network usage.
Host earnings are generated through a combination of usage-based fees and token incentives. According to the lite paper, a 7 kW Beast charger priced at $599 and delivering 100 kWh/day could generate approximately $15.93 in daily net profit, with breakeven in ~75 days and annual net earnings around $2,900.
Fees from each session are distributed as follows: 70% to the charger owner, 30% to DeCharge, with 10% of that 30% allocated to EV driver incentives. Pricing is determined by each host and may vary based on location, demand, and electricity costs. Payments are currently accepted in Fiat and USDC on Solana.
Source: DeCharge Network
Token rewards are calculated using a dynamic formula that accounts for multiple factors, including energy dispensed, uptime, reliability, deployment timing, and charger location. Higher rewards are issued to consistently active chargers deployed early or placed in underserved areas. Devices with low availability or poor placement receive minimal rewards.
Over time, DeCharge may expand monetization opportunities to include:
- Advertising: Some chargers may support digital displays for sponsored content.
- Service Co-location: Hosts may sublease charger space to complementary services (e.g., battery swaps, vendors).
- Energy Resale: Future participation in vehicle-to-grid (V2G) or peer-to-peer energy markets could enable hosts to sell excess or buffered energy.
Additionally, DeCharge has explored the tokenization of deployed chargers as real-world assets (RWAs). This would allow for fractional ownership of charging infrastructure and enable transparent, onchain distribution of usage-based revenue. Such a model could support more granular infrastructure financing and broaden participation beyond direct hardware operators.
Host profitability will vary based on local conditions such as electricity prices, traffic density, and site accessibility. Returns are not guaranteed, and the future value of token rewards remains uncertain.
On the demand side, EV drivers benefit from a more widely distributed and accessible charging network, reducing travel time to the nearest station and improving overall availability. Token-based rebates may also offset charging costs. This incentive structure aligns the interests of users, hosts, and the protocol, supporting gradual and demand-driven network expansion.
Ecosystem and PartnersDeCharge is developing a broader ecosystem beyond EV charging, integrating with other decentralized infrastructure networks to enhance functionality and resilience. Key partnerships span data processing, smart energy optimization, geolocation services, and hardware manufacturing.
- Linera: In October 2024, DeCharge announced a collaboration with Linera, a Layer-1 network focused on scalable microchains. Linera’s infrastructure enables parallel transaction processing off of Solana, which DeCharge uses to offload user charging-related data such as session records, station uptime, and energy metrics. These logs are processed on Linera and periodically anchored to Solana for settlement and transparency. This design aims to calculate rewards and incentives, improve system responsiveness, and handle high-volume data without congesting the Solana network.
- DePHY Network: DeCharge has partnered with DePHY, a decentralized energy management protocol, to co-deploy the Open Source Energy Module (OSEM) in each Beast charger. This allows the device to function simultaneously as a DePHY node, supporting local energy optimization tasks such as dynamic load balancing, battery management, and renewable energy prioritization. These capabilities lay the groundwork for future applications like vehicle-to-grid (V2G) participation and local energy trading.
- GEODNET: In late 2024, DeCharge launched a deployment initiative with GEODNET, a decentralized GNSS network offering RTK corrections for sub-meter GPS precision. The initiative combines a GEODNET base station, DeCharge Beast charger, and DePHY node at a single site, enabling hosts to earn rewards from all three networks and encouraging cross-network deployment across the DePIN landscape.
- Community and Developer Ecosystem: DeCharge has participated in regional Solana-focused developer initiatives, including the Superteam Founders Villa pitch in the UAE. It has also engaged with grassroots communities in India and Southeast Asia to support local deployment and onboarding. The project is a participant in the DePIN Alliance and regularly shares updates and collaborate with other infrastructure networks to align on standards and adoption strategy.
- Hardware and Manufacturing: While specific manufacturing partners have not been disclosed, DeCharge is actively producing and distributing its core hardware models, the 7 kW Beast, and the 60 kW Titan-60. The team has indicated ongoing work across the U.S., Europe, and Asia, with attention to regional energy compliance requirements and hardware customizations for markets such as India and the Middle East.
Following its seed round and initial deployment traction, DeCharge has outlined a roadmap for 2025 focused on global scaling, product upgrades, token rollout, and regulatory alignment.

Source: DeCharge Network
- Deployment and Expansion: DeCharge plans to expand its charger network across Asia, the Middle East, Europe, and North America, with early growth centered in India. The team is prioritizing growth in India, where pilot programs began, and is onboarding deployment partners in additional regions. Site selection is supported by H3 geospatial indexing to avoid charger clustering and prioritize underserved areas by growing EV density.
- Hardware Iteration: A second-generation Beast charger is in development, featuring integrated energy storage (~11 kWh) to enable continued operation during grid disruptions or in off-grid environments. The 60 kW Titan-60 DC charger is expected to enter broader deployment, targeting highways and commercial zones. The team is also evaluating the need for mid-range chargers tailored to two-wheelers and micro-mobility fleets, particularly in emerging markets.
- Token Launch and Marketplace: DeCharge’s native token is yet to launch. A public rollout is planned once the network reaches sufficient charger adoption and usage. The token will support the DeCharge Energy Marketplace, enabling peer-to-peer functions such as credit resale, discounted off-peak charging, and tokenized clean energy transfers. Rollout will initially target jurisdictions with supportive crypto regulation.
- AI and Automation Features: Planned AI-based features include dynamic pricing adjustments, charger health diagnostics, and smart routing for users. A recommendation engine is expected later in 2025 to help optimize charging behaviors and station availability. Aggregated network data will support demand forecasting and operational planning.
- Partnerships and Regulatory Engagement: DeCharge is engaging with local regulators and infrastructure partners in key markets to support long-term growth and compliance. Potential B2B integrations include fleet operators, ride-hailing services, and real estate developers seeking to incorporate EV charging into new properties. These commercial efforts complement the project’s grassroots host onboarding strategy, combining top-down and bottom-up expansion approaches
DeCharge is building a decentralized EV charging network that enables individuals and small businesses to host internet-connected chargers and earn usage-based and tokenized rewards. The system integrates blockchain coordination, geospatial deployment tools, and incentive mechanisms to expand infrastructure access, particularly in underserved regions.
Backed by a $2.5 million seed round led by Lemniscap in March 2025, DeCharge has formed partnerships with DePHY and GEODNET and is exploring the use of microchain infrastructure (e.g., Linera) to support high-frequency data processing. Early deployments have logged over 1.3 million charging minutes and have begun to validate the network’s incentive design and ROI model for node operators.
Looking ahead, DeCharge plans to scale its charger network, launch a second-generation AC unit with integrated energy storage, and introduce its native token to support a peer-to-peer energy marketplace.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.