and the distribution of digital products.
State of Tezos Q2 2024
- The Tezos team launched Tezos X, a roadmap for the future of the Tezos ecosystem. It focused on enhancing scalability with a new concept called “Canonical Rollup” and expanding ecosystem versatility through support for mainstream programming languages, composability, and interoperability.
- Etherlink mainnet beta launch in May 2024. Etherlink is a non-custodial, EVM-compatible, fast, fair and low-cost Layer-2 blockchain powered by Tezos Smart Rollups. Etherlink Mainnet beta is the final stage before launch.
- The Paris upgrade was successfully implemented. It introduced 10-second block times, adaptive issuance, and the Data Availability Layer (DAL), which enhanced network performance.
- Total value locked (TVL) in USD decreased by 15% QoQ, but TVL in XTZ terms rose by 42%, showing that the decline was driven by lower asset values, not withdrawals.
- Tezos ranked 44th with 228 developers as of July 2024, according to Electric Capital.
Tezos (XTZ) is a Liquid Proof-of-Stake (LPoS) blockchain network known for its strong focus on security, upgradeability, and democratic community governance. Its smart contracts are implemented using the Michelson language, designed to facilitate formal verification while also offering Ethereum virtual machine (EVM)-compatibility through Etherlink, a community-supported Layer-2. The network features onchain governance and self-amending functionality, enabling stakeholders to vote on protocol upgrades without requiring a network hard fork. Recent upgrades on Tezos have focused on scalability and performance through Smart Rollups and a Data Availability Layer (DAL). The Mumbai protocol upgrade introduced Smart Rollups, a Layer-2 scaling solution that enables higher throughput beyond 1 million TPS on Layer-2 and customization to adapt to specific use cases, such as implementing new coding environments. The Oxford 2 protocol upgrade added private Smart Rollups, allowing developers to implement permissioned Layer-2 solutions, which is significant for enterprise and government sectors. The Paris Upgrade introduced DAL infrastructure built to run on top of Tezos' Layer-1, ensuring data availability and security across the scaling infrastructure. It also implemented Adaptive Issuance, which adjusts token issuance based on the ratio of staked XTZ to the total supply.
In Q2, Tezos launched Tezos X, which focuses on boosting blockchain versatility through composability and interoperability. Leveraging Smart Rollups, Tezos X enables developers to create more complex applications with customizable programming environments and improved connectivity across the Tezos ecosystem, getting close to a cloud-like user experience for blockchain users.
Website / X (Twitter) / Discord
Key Metrics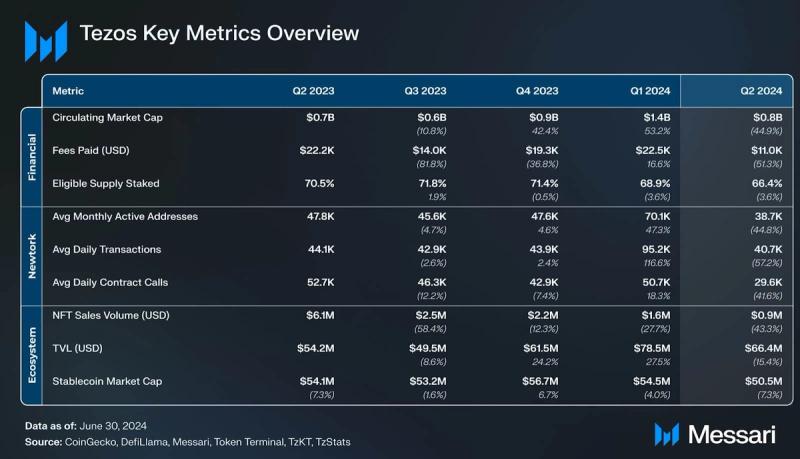 Financial Overview
Financial Overview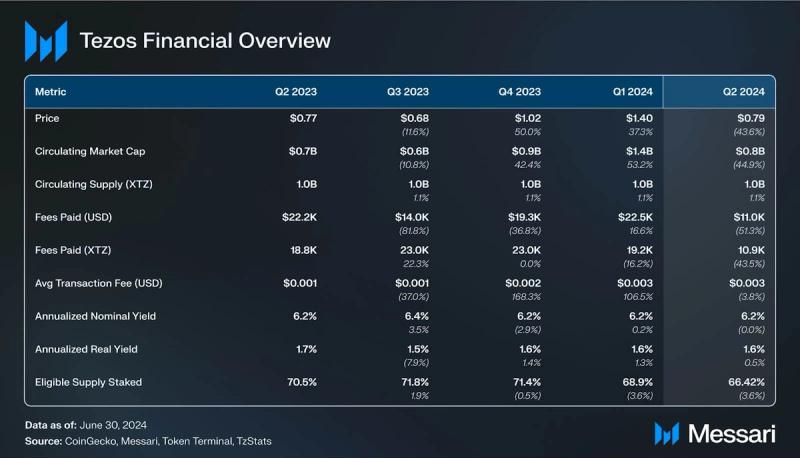 Market Capitalization and Revenue
Market Capitalization and Revenue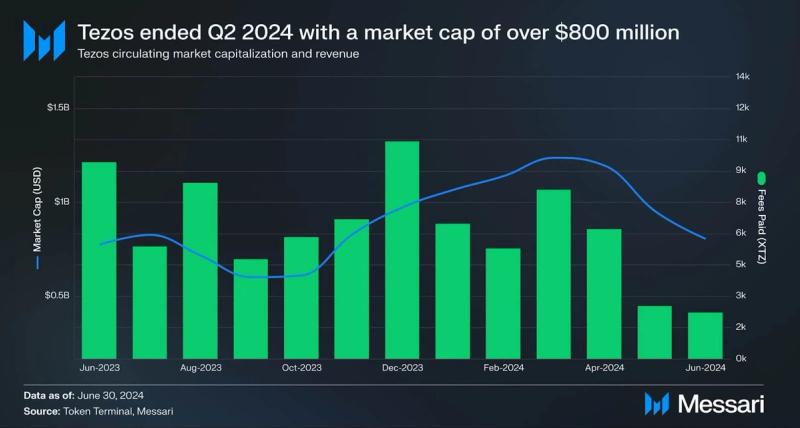
In Q2, Tezos saw a decrease in transaction fees, paid by users to transact on the network, which fell to $11,000—a 51% drop QoQ. This decrease was partly due to the introduction of Smart Rollups, designed to shift activity to Layer-2 and lower the overall fees collected. Additionally, Tezos' market cap dropped to $800 million, down 44.9%, reflecting a broader cooling in the crypto market following the March highs.
SupplyNative token, XTZ is used as a medium of exchange and for staking, delegating, and facilitating governance. As of the end of Q2, the current circulating supply of 1.0 billion XTZ. The Mumbai upgrade adjusted the block time to 15 seconds and reduced block rewards to 20 XTZ to maintain the annual inflation rate. The Paris upgrade introduced Adaptive Issuance, a dynamic mechanism that adjusts staking rewards to maintain network security with minimal inflation. This system targets a 50% staking ratio of the total Tezos supply, adjusting rewards to encourage more or less staking as needed, thereby reducing inefficiencies and aligning Tezos with real-world use cases. The annualized real yield for validators remained at 1.6%, with a QoQ increase of 0.5%.
Network Overview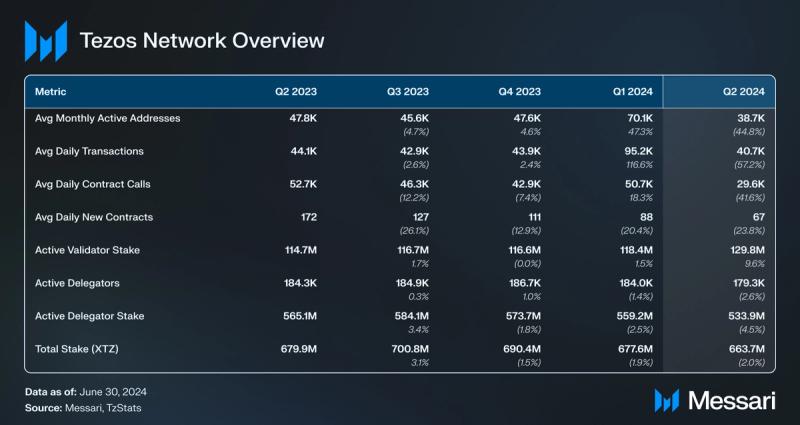 Usage
Usage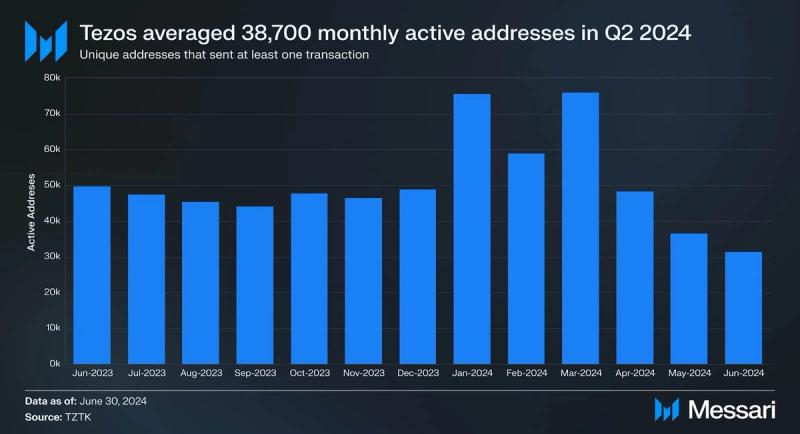
In Q2 2024, the average monthly active addresses dropped to 38,700, a 45% decline QoQ. However, this is only a 19% decrease compared to the same period last year, with Q1 2024 reaching all-time highs. Notably, in May 2024, Layer-2 solution Etherlink launched its mainnet beta, aiming to reduce fees and improve transaction speeds. It has since experienced significant user growth, with over 90,000 unique wallets since launch.
Network UpgradesSmart RollupsTezos Smart Rollups allow development of rollups using any programming language that can be compiled into WebAssembly (WASM), such as Rust, C/C++, and Go. Etherlink is the first EVM-compatible non-custodial Smart Rollup. This opens opportunities for developers using other programming languages and virtual machines to contribute to the Tezos ecosystem.
The Q1 2023 Mumbai upgrade introduced Smart Rollups, allowing for the creation of applications on a Tezos Smart Rollup using any language compatible with WebAssembly. The Q2 2023 Nairobi upgrade expanded the capabilities of Smart Rollups, such as internal Layer-2 messages allowing it to sync with Tezos protocol upgrades. The Q1 2024 Oxford 2 upgrade introduced Private Rollups, which allow developers to choose between public and permissioned L2s. The Octez V19.0 upgrade in Q1 2024 made rollup nodes protocol-agnostic, meaning that they can smoothly handle Tezos protocol upgrades.
Jstz is a proposed rollup that enables the use of JavaScript for building and deploying smart contracts. Jstz aims to lower the barrier of entry by bringing a familiar Web2-like experience with Web3 benefits, expanding Tezos' reach by tapping into JavaScript tools and libraries.
Paris UpgradeOn June 4, 2024, the Paris B protocol upgrade was activated, marking the 16th major enhancement to the Tezos blockchain. This upgrade brought several key improvements designed to bolster the network's performance and security. Notably, it reduced block times to 10 seconds and introduced the Data Availability Layer (DAL) on the mainnet, a critical step in enhancing throughput for Smart Rollups. Additionally, refinements to the Tezos Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism were made to improve the network's scalability and economic sustainability, further positioning Tezos as a leading, efficient blockchain platform.
However, the Paris B upgrade also encountered challenges, particularly with the Smart Rollups feature. A critical bug emerged, affecting withdrawals from Etherlink to Tezos Layer-1, which prompted a swift response from Nomadic Labs. They developed an emergency bug fix, Paris C, which was quickly implemented through a User-Activated Upgrade (UAU) and included in the Octez V20.1 release. The ParisC fix was successfully activated on June 25, 2024, at block 5,898,241, showcasing Tezos' agility in addressing and resolving issues to maintain network stability.
EtherlinkEtherlink, the first EVM-compatible non-custodial Smart Rollup on Tezos, entered mainnet beta in May 2024. It facilitates the deployment of EVM-based contracts on Tezos and offers full compatibility with the Ethereum ecosystem (e.g., MetaMask wallet connectivity). In addition, it features low fees, low latency, and increased security with permissionless fraud proofs. Etherlink is implementing full decentralization: onchain governance controls both upgrades and sequencer operators. Etherlink will integrate with Tezos' L1 protocol, promoting interoperability and functional expansion in the ecosystem.
Etherlink supports a range of developer tools, including oracles, DeFi solutions, indexing, and privacy tools. Recent additions to the suite of tools supported on Etherlink are:
- Pyth Network: an oracle provider supporting price feeds on Etherlink.
- Blockscout: has built an Etherlink blockchain explorer.
- Transak: provides on and off ramp services converting fiat to crypto.
- Omnisea: will support no-code NFT launching services on Etherlink.
- Subsquid: a decentralized data lake, announced support for their tools on Etherlink, including their Subquid SDK.
- OnChainVision Labs: provides a suite of tools to launch, manage, and tokenize digital assets.
Tezos X leverages Smart Rollups and DAL to provide a comprehensive upgrade design. The upgrade was introduced at TezDev 2024 with goal of making the Tezos Ecosystem a more versatile and efficient platform. Tezos X aims to enhance the blockchain's utility and competitiveness by focusing on two key areas: composability and interoperability.
Composability allows applications to interact and create a sum greater than their individual parts. This is achieved through a unified rollup system, where smart contracts can interact across different environments.
Interoperability opens up the Tezos ecosystem to new programming environments and connects with other blockchains and non-blockchain systems. This "plug'n'play" approach allows developers to use their preferred languages and tools to build applications that can interact across different platforms and systems.
Tezos X also features the canonical rollup, a unified rollup designed to support multiple execution environments. It allows developers to deploy smart contracts in their preferred programming languages — in other words, a smart contract written in Solidity can interact with one written in Python and pass results to another in JavaScript, all within the same transaction and the same rollup.
Additional DevelopmentTezos is a smart contract Layer-1 network, allowing complex applications to be built on top of it. These applications can serve various purposes, including decentralized finance, NFTs, gaming, identity, enterprise, and more. Select development updates from Q2 include:
- Tezos Unity SDK: Simplifies large-scale gaming development. Gaming developer, Baking Bad, launched a third-person shooter.
Grant Programs and Investments: The Tezos Foundation supported various development projects, including infrastructure and tooling enhancements. Some investments from Q2 include:
- Fraktion: A real-world asset (RWA) protocol that allows easier access to real estate.
- Lyzi: A mobile crypto payments application.
- ASCS (Automotive Solution Center for Simulation): A non-profit hub that collaborates with leading automotive brands like BMW to enhance membership management, partnering with Altme and Tezos for innovative digital identity solutions.
- idOS Consortium: Tezos was a part of the $4.5 million funding round for idOS, a Web3 identity layer. IdOS enables compliant user onboarding, reducing friction, giving users control over their data, and unlocking self-custodial debit cards and bank accounts.
According to Electric Capital’s report, Tezos had 72 full-time developers and 228 monthly active developers on July 1, 2024.
Security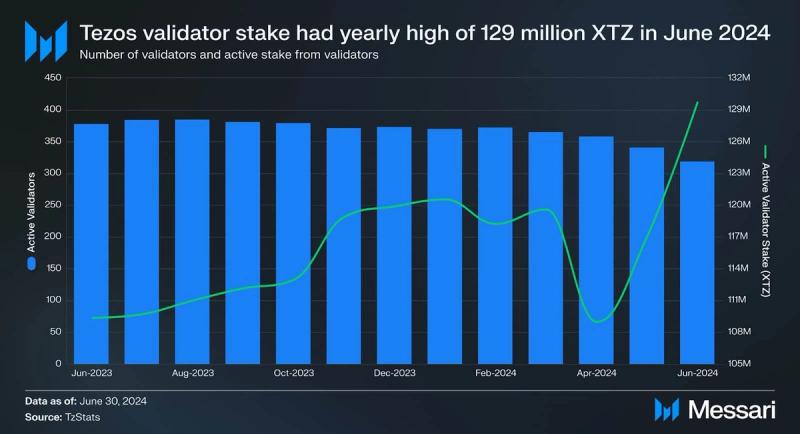
Tezos uses a Liquid Proof-of-Stake mechanism, which requires validators (known as “bakers” in the Tezos ecosystem) and delegators to stake XTZ as collateral to secure the network. Rewards and fees collected from transactions are paid to validators and delegators for maintaining the network. Active validators and active validator stake have remained consistent over the last three quarters. In Q2, active validators saw a 12% decrease, but active stake increased by 9.6%, QoQ. Active validator stake reached a yearly high of 129 million XTZ.
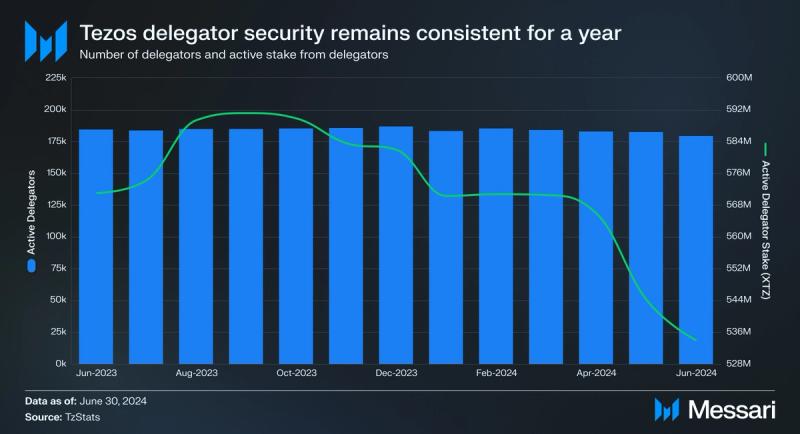
Delegators stake XTZ on active validators and receive a portion of fees and rewards collected. Active delegators and stake from delegators decreased in Q2, by 2.6% and 4.5% QoQ, respectively.
Adaptive Issuance dynamically adjusts the issuance of XTZ based on the proportion of staked tokens to the total supply. At the end of each blockchain cycle, the issuance rate is modified to target a protocol-defined staking level, currently set at 50%. This mechanism incentivizes staking to provide stable security for the network.
While Smart Rollups are dependent on Layer-1 security for settlement, they also benefit from Tezos validators to determine input transactions on Layer-2. The Tezos network has shown consistent year-over-year stability in the number of validators and delegators, as well as in staked XTZ. This stability is crucial for secure and scalable Layer-2 growth. Validators in the ecosystem are also decentralized geographically and by host service providers, further ensuring the network's resilience and security.
GovernanceTezos utilizes a Liquid Proof-of-Stake mechanism, enabling staked XTZ to be used for both network security and governance. The network's self-amending blockchain reduces the need for hard forks by employing onchain governance for protocol upgrades. Users delegate their XTZ to validators who participate in stake-weighted voting. The governance process is divided into five periods, spanning approximately 2 months and 10 days.
To complement governance, Tezos Commons established the Tezos Ecosystem DAO, which manages and allocates XTZ for community projects. The DAO’s initial funding came from NFT sales on Objkt and donations from ecosystem participants.
Etherlink follows a governance model similar to Tezos Layer-1, ensuring fairness and transparency. Governance for Etherlink is self-amending (meaning no hard fork) and all stages are conducted onchain. The governance process consists of three stages: a Proposal period, a Promotion period enforced by the governance contract on Tezos Layer-1, and a Cooldown period enforced by Etherlink. The Etherlink governance periods are synchronized with Layer-1 governance periods. The first upgrade for Etherlink was implemented successfully shortly after launch.
Ecosystem Overview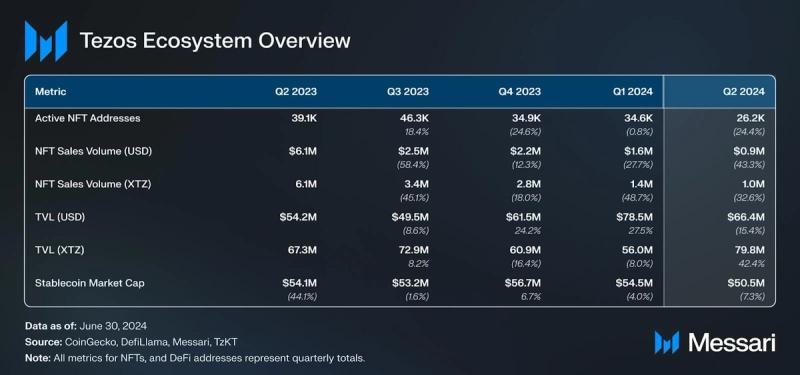 Etherlink Adoption
Etherlink Adoption
Following the launch of Etherlink mainnet beta, developers have begun building within the EVM environment, integrating their applications into the broader Tezos ecosystem. The Etherlink ecosystem currently has 50+ projects building towards launch, with over 15 live on Testnet Beta Mainnet. Q2 saw the development of various applications on Etherlink, including:
- Bit Hotel: A social open-world hotel-casino-themed game, built in collaboration with Gaming Vertical.
- Degenerator.wtf: A user-friendly platform for creating memecoins, designed to bring the memecoin economy to Tezos.
- OrganicGrowth.wtf: A no-code platform for launching tokens and memecoins, helping builders expand their communities.
- Tachyswap: An automated market maker (AMM) decentralized exchange (DEX) that enables permissionless trading of all assets on Etherlink.
- Defi Catalyst Accelerator (DCA): A Singapore-based accelerator program committed to development of the Etherlink Ecosystem. Their first batch of DeFi builders included: Rivo (DeFi yield marketplace), SaveX (self-custody Web3 wallet), Superlend (lending and borrowing aggregator), Hanji (onchain order book), and StableTech (DeFi platform for stablecoins, lending, and DEX.
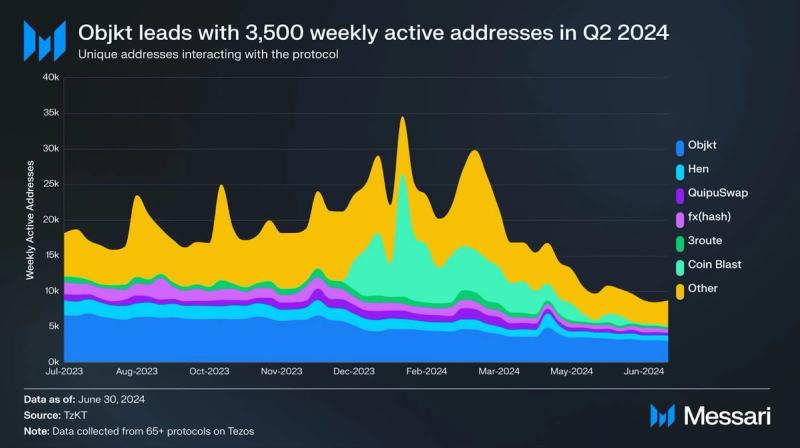
The art marketplace Objkt dominated the Tezos NFT network, with an average of 3,500 weekly active addresses and capturing 35% of the market share of users. NFT sales dropped 43% QoQ in Q2 2024, totaling $912,000, while unique active users fell 24% to 26,000. This decline mirrors a broader trend across NFT markets, with Ethereum-based NFT sales down 61% between Q1 and Q2 2024.
Development in the NFT ecosystem remained strong in Q2:
- Art on Tezos: In Motion showcase at NFC Lisbon featured the creative talent of moving image works across the Tezos ecosystem on a 360° screen to a packed audience.
- Curation: at the Digital Art Mile in Basel during Art Basel, showcased Objkt and fxhash booths along with a live minting experience by Tesserart.
- Museum of Moving Image Partnership: a 12-month collaboration between MoMI and the Tezos Foundation, offering digital artists an opportunity to exhibit their work in a museum. Visitors could mint and take home a fragment of the artwork for free.
- Proof of Participation Tokens: Launched at the Serpentine for Judy Chicago’s interactive project, ‘What if Women Ruled the World?’, running until September 1.
- Objkt Generative Minting Feature: Unveiled with a p1xelfool collection in collaboration with Fakewhale, selling over 500 editions and generating over 10,000 XTZ in sales volume to date.
- fxhash Vertex Drop: The first curated drop "Entangled" by Bjorn Staal sold out, generating over 60,000 XTZ in sales.
- Kim Asendorf’s C0L0RGRiD SE17: sold for 20,000 XTZ on the secondary market.
- Art on Tezos x Artcrush: screened art on over 1000 billboards across Belgium during EthCC and TezDev, along with a physical exhibition.
- World of Women: Art community that promotes gender parity and opportunities for women in Web3 joins the Tezos ecosystem.
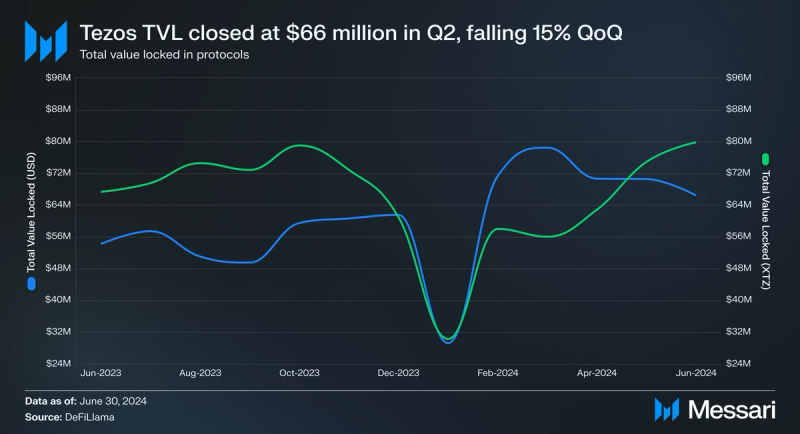
Total value locked (TVL) in USD fell by 15% QoQ in Q2 2024, closing at $66 million. This decline was driven by the drop in XTZ's price, since TVL in XTZ increased by 42% QoQ. The dynamic indicates that the decrease was due to decrease in asset value, rather than withdrawals from protocols.
Most TVL in crypto exists on EVM-compatible networks. With the launch of Etherlink, developers now have the opportunity to deploy EVM-compatible protocols on Etherlink, enabling them to potentially attract communities within the Tezos ecosystem. The launch of Etherlink benefits the Tezos ecosystem by drawing in users and builders from other EVM-compatible networks, thereby expanding its exposure to the largest pool of activities in the DeFi space.
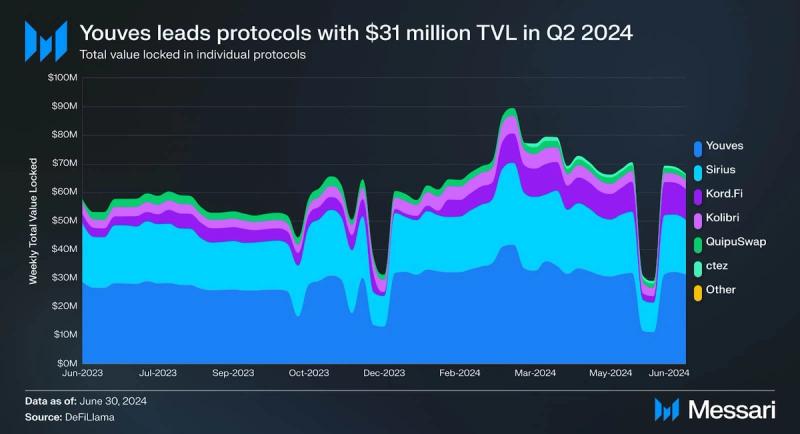
Youves, a decentralized synthetic assets application, is the largest protocol by TVL, securing $31 million in assets. Sirius, a liquidity-baking protocol for XTZ/tzBTC pools, had the second-largest TVL at over $19 million. Kord.Fi, another liquidity-baking protocol for XTZ-tzBTC, had the third-largest TVL with over $10 million. With the capital efficiency improvements in tzBTC 2.0, these liquidity-baking protocols may provide additional incentives and thus increase their TVL.
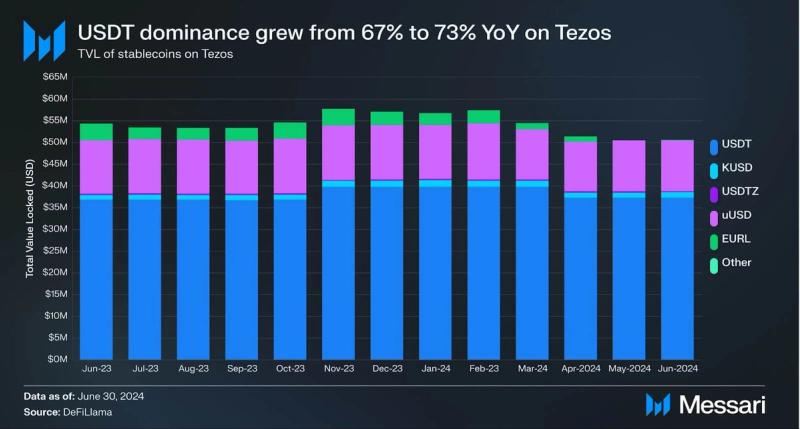
Tether’s USDT increased its dominance in the stablecoin market year-over-year, going from 67% to 73% of all stablecoins. Tether had over $37 million in USDT issued on Tezos by the end of Q2. The largest stablecoins exclusively issued on Tezos were Kolibri’s kUSD and USDTez’s USDtz, which had over $1 million and over $275,000 in stablecoins issued, respectively.
GamingQ2 2024 marked substantial progress in gaming protocols on Tezos. With Tezos X aiming to achieve 1 million transactions per second on Layer-2 and offer composable development environments, gaming developers have shown increasing interest in launching their games on Tezos. Gaming development highlights from Q2 include:
- TapNation: A leading publisher with over 1 billion downloads, launched Athletic Rush, in collaboration with Gaming Vertical.
- BlockGames: Partnered with Tezos to integrate mobile games into the BlockGames ecosystem.
- Metapals: An AI-companion game partnered with Sanrio, the creators of Hello Kitty, and British children’s program Teletubbies. Minting for NFT companions launched in May 2024, with over 1,000 Teletubby NFTs sold.
- OpenPad and GameFi: Launchpads that help developers gain funding, integrated with Tezos and Etherlink.
- Stables: Tezos Foundation announced an investment in Stables, a Web3 horse racing game, joining PMU, the European leader in horse betting.
In June 2024, Tezos unveiled their proposed roadmap, Tezos X. Utilizing Smart Rollups and DAL to create composable and interoperable development environments for the Tezos Ecosystem. Key milestones in this roadmap include:
- Q3 2024: Etherlink rollup launched
- Q3 2024: MEV protection — equencer on rollups guarantees the absence of manipulation and protection from maximum extractable value (MEV).
- Q4 2024: Etherlink + DAL, allowing high throughput communication between sequencer and Etherlink Rollup.
- 2025: Michelson Rollup: Execution environment compatible with Tezos Layer-1 and instant asset transfer to Etherlink.
- 2025: JavaScript Rollup: execution environment using JavaScript. First JavaScript applications launched.
- 2026: Canonical Rollup: Integrated execution environment with instant transactions across applications written in different programming languages.
- 2026: Smart Contract Migration: Applications begin to migrate from Layer-1 to a Smart Rollup, leaving decentralization-sensitive applications in Layer-1.
- Beyond 2026: 1 million transactions per second on Smart Rollups and 5s block times on Layer-1.
Q2 2024 was a period of significant development and strategic advancements for the Tezos ecosystem. The unveiling of Tezos X marked a pivotal step forward, emphasizing the importance of composability and interoperability to drive future growth. This upgrade, combined with the introduction of Smart Rollups, positions Tezos to handle more complex applications and attract a broader range of developers. Despite a decline in transaction fees and market cap, primarily due to market-wide cooling and the strategic shift to Layer-2 solutions, the ecosystem remained resilient with strong developments in gaming, DeFi, and art and NFTs.
As the first EVM-compatible rollup on Tezos, Etherlink's mainnet beta launch in May opened new avenues for EVM-based developers to integrate with Tezos, reflecting the network's growing interoperability and appeal. Throughout these changes, Tezos continued to foster its ecosystem through strategic partnerships, grant programs, and new initiatives, underscoring its commitment to long-term growth and innovation.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.