and the distribution of digital products.
State of Polkadot Q4 2024
- Polkadot’s monthly transactions rose from 20 million in January to nearly 60 million in November 2024. This 200% increase was driven by strong performance from rollups like Neuroweb and Frequency.
- Polkadot improved interoperability after launching Snowbridge, a trustless Polkadot-Ethereum Bridge and Hyperbridge, which leverages zk-proof and coprocessor technology to securely transfer assets across multiple chains, including Ethereum, Optimism, Arbitrum, Base, BNB, and Gnosis.
- Polkadot’s Spammening test on its live sister network, Kusama, reached 143,343 TPS at 23% capacity, with a projected 623,000 TPS at full utilization. The network maintained stable performance under heavy loads.
- Polkadot remains a leading hub for blockchain innovation and supports over 1,200 monthly active developers who benefit from its native SDK, previously called Substrate.
- DOT’s market capitalization rose by 71% QoQ to a two-year high of $16.4 billion and signaled strong investor confidence.
Polkadot (DOT) is a distributed blockchain computing platform that acts as a base layer for other sovereign blockchains, initially called parachains, for validation and shared security. Polkadot was built using Substratet, a blockchain developmental framework now better known as Polkadot SDK. Furthermore, Polkadot’s base layer is known as the Polkadot Chain (aka Relay Chain), which utilizes a Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) consensus mechanism, and its state machine is compiled to WebAssembly (Wasm).
The Polkadot Chain’s core function is to validate and provide security to its rollups. Agile Coretime, released during Q3 2024, enhances the network’s scalability, cost-efficiency, speed, and flexibility by dynamically allocating computational resources. This feature replaces the previous system of leasing single cores through auctions with an on-demand blockspace model, adjusting resource availability based on network demand. This approach helps prevent resource wastage during periods of low activity and mitigates congestion during peak times.
Lastly, parachains (rollups) on Polkadot can communicate with one another through the Cross-Consensus Mechanism Format (XCM). The XCM is a messaging format that standardizes messages between Polkadot’s chains, allowing for greater interoperability.
Website / X (Twitter) / Discord
Key Metrics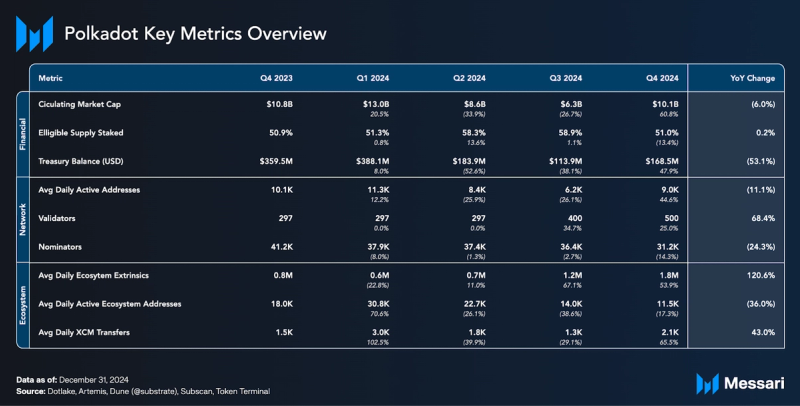 Ecosystem Analysis
Ecosystem Analysis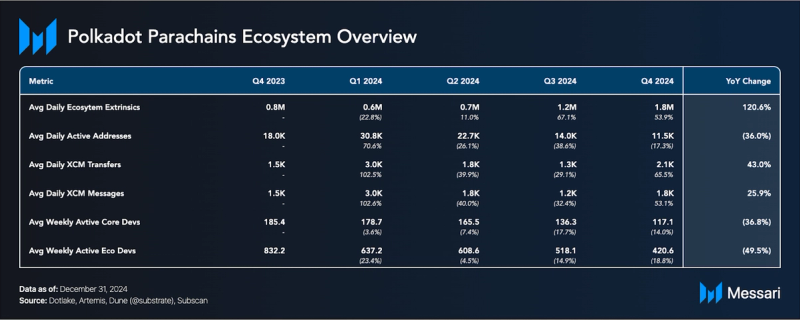 Rollup Extrinsics
Rollup Extrinsics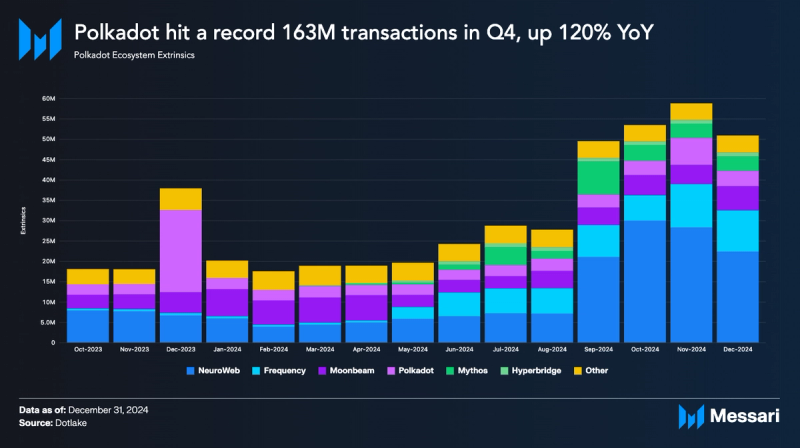
Transaction activity across the Polkadot ecosystem increased sharply in the second half of 2024 and rose by approximately 200%. Monthly transactions grew from 20 million in January to nearly 60 million in November 2024. Neuroweb, developed by Origin Trail, led in Q4 2024 with an average of 26 million monthly transactions and recorded a 136% QoQ increase from 12 million in Q3. Frequency also experienced a surge in activity and rose from a monthly average of 7 million monthly transactions in Q3 to a monthly average of 9 million in Q4. Phala, Litentry, and Mythos also contributed to Polkadot’s increasing transaction volume.
This surge in activity was further fueled by the adoption of cross-chain bridges like Snowbridge. This trustless bridge, connecting Polkadot and Ethereum, launched in June 2024 and has seen considerable adoption, with TVL exceeding $70 million by 2024 year-end. Snowbridge allows token transfers between the two networks, which contributed to the overall increase in transaction volume on Polkadot. Its key features, such as community ownership, trustless operation, and XCM compatibility, have made it a popular choice for users looking to move assets between Polkadot and Ethereum.
On November 7 2024, Polkadot introduced Hyperbridge, the first verifiable, multichain bridge connecting Polkadot, Ethereum, Optimism, Arbitrum, Base, BNB, and Gnosis. Hyperbridge improves blockchain interoperability by utilizing a coprocessor model for complex computations and employing zk-proofs with onchain finality validation to strengthen security. Two testnet cycles proved Hyperbridge's effectiveness, which processed over 600,000 cross-chain messages. Sixty-six independent relayers validated the network. This approach tackles security challenges associated with traditional cross-chain approaches, such as differences in consensus mechanisms and data mobility.
The interoperability approaches introduced this quarter have strengthened Polkadot's utility and set a benchmark for cross-chain communication. As these technologies continue to mature and gain adoption, Polkadot is well-positioned to support a more interconnected and efficient decentralized ecosystem.
XCM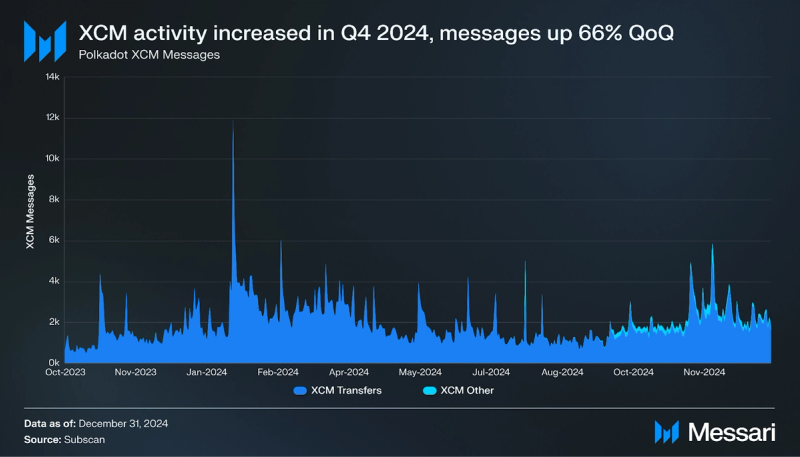
The Cross-Consensus Message Format (XCM) is a standardized messaging format and language that enables seamless communication between rollups and other consensus-driven systems. XCM plays a crucial role in facilitating interoperability and complex cross-consensus interactions. It allows blockchains to exchange messages, perform operations, and transfer assets, among other use cases.
In Q4 2024, Polkadot’s XCM activity increased. Daily XCM transfers averaged 1,841 (+53% QoQ), and other messages averaged 255 daily (+300% QoQ). With an average of 2,096 per day, total daily XCM messages increased by 66% QoQ.
The quarter saw an expansion of high-yield farming opportunities across the Polkadot ecosystem. Bifrost launched a 1 million DOT incentive program in October 2024, which targeted liquidity pools on platforms like StellaSwap and Beamswap. The impact was immediate, with the BNC-DOT pair on StellaSwap reaching a 423% Annual Percentage Rate shortly after the program's launch.
The success of these incentive programs was evident in the rapid growth of TVL across various pools. For instance, the vDOT-DOT pool on StellaSwap experienced a twentyfold increase in TVL, reaching $622 million by late October, while still maintaining a 19.92% APR.
Rollup Addresses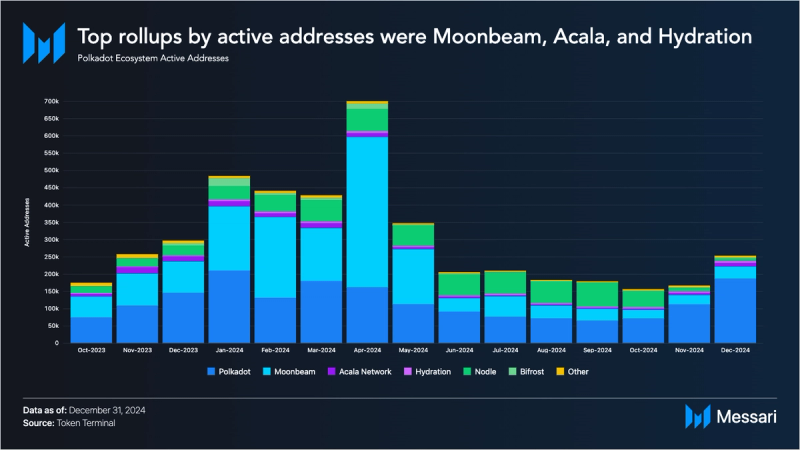
Despite the rise in transaction volume during Q4, active addresses in the Polkadot ecosystem declined. The average number of daily active addresses fell to 11,500 in Q4 from 14,000 in Q3. In Q4 2024, the average monthly active addresses on Polkadot’s Relay Chain reached 122,919, while rollups recorded an average of 68,847. Among rollups, Moonbeam, Acala, and Mythos ranked highest by active addresses with market shares of 15%, 3.6%, and 2.7% respectively during the quarter.
Development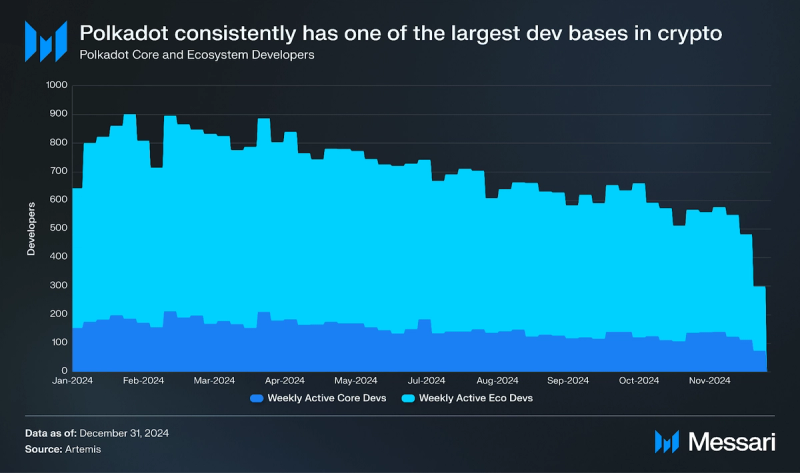
Polkadot boasts one of the largest developer bases in the crypto industry. According to Electric Capital, in October 2024, Polkadot had 1,261 monthly active developers, with 460 of them classified as full-time, placing the network fourth behind Ethereum, Base, and Polygon. Artemis also tracked developer data and reported an average of 117 weekly active core developers and 420 active ecosystem developers in Q4 2024.
Financial Analysis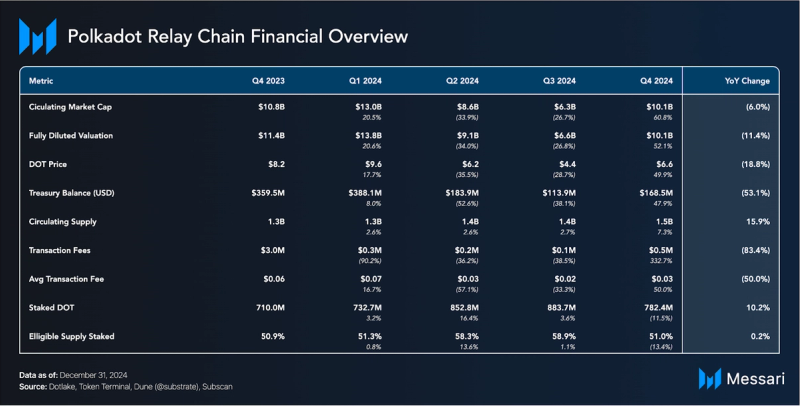 Market Capitalization
Market Capitalization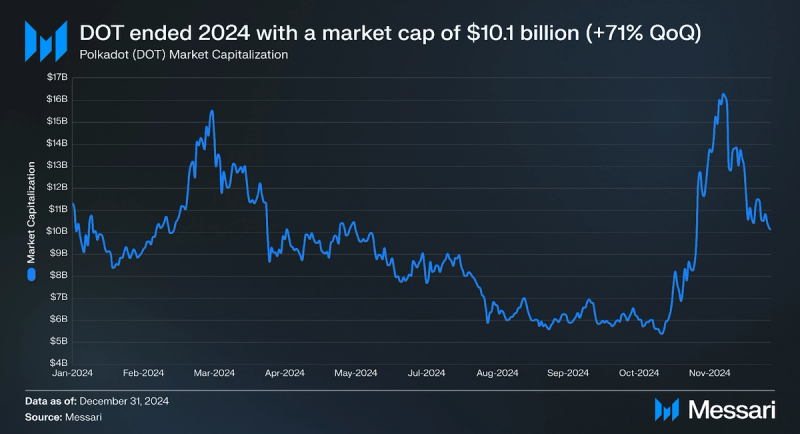
After cooling off with the broader market in Q3 2024, DOT’s market capitalization expanded in Q4. During Q4 2024, DOT’s market capitalization increased 71% QoQ, from $6.2 billion to $10.2 billion. It peaked in early December at $16.4 Billion — a two-year high. DOT’s market cap rank shifted from 16 to 19 during Q4 2024, ranking it above Bitcoin Cash and Pepe.
Transaction Fees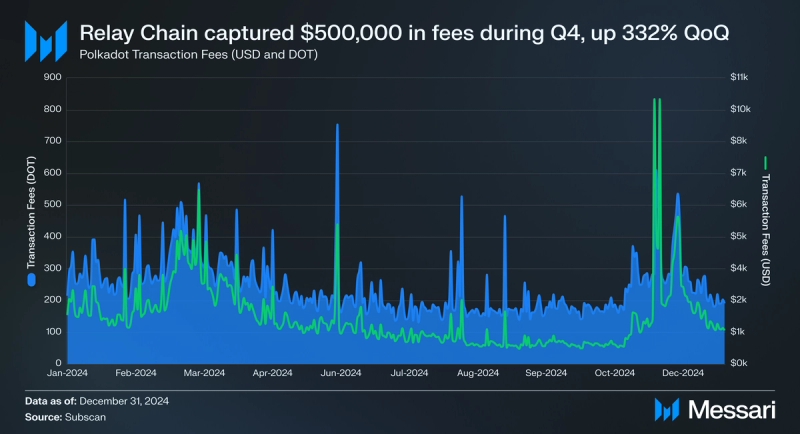
The Polkadot Chain’s total transaction fees tends to be relatively lower compared to its competitors due to the network's structural design. In Q4 2024, the Relay Chain benefitted from Polkadot's ecosystem increasing transaction volume. The Relay Chain went from capturing $113,737 in fees in Q3 to $492,141 in Q4, a 333% QoQ increase. The average transaction fee increased from $0.02 to $0.03.
Treasury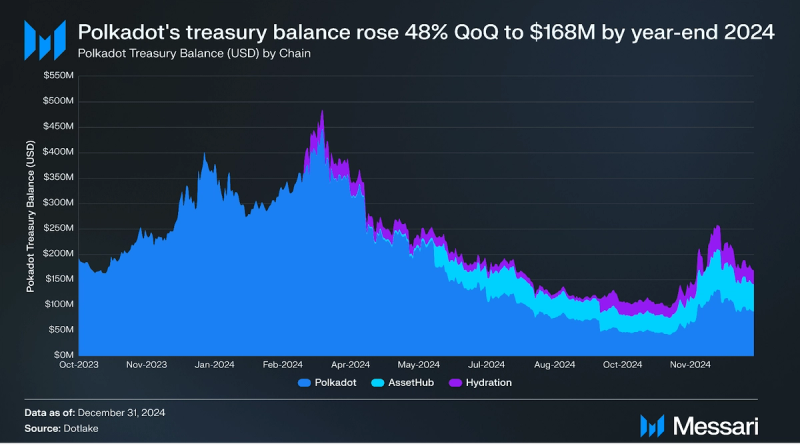
The Polkadot Treasury is financed through block rewards, validator slashing, transaction fees, and staking inefficiencies. Treasury funds held in a system account are allocated for expenditures within a 24-day spend period, with any unspent funds subject to a 1% burn. Notably, all treasury expenditures are executed automatically on-chain. The passage of OpenGov has transformed the referendum lifecycle and decentralized the decision-making process, leading to increased treasury activity.
The Polkadot Treasury expanded its asset distribution across the relay chain, Asset Hub, and the Hydration chain to manage assets such as DOT, USDT, and USDC. According to Dotlake, Treasury spending in 2024 increased 3.2 times compared to 2023. Allocations included $58.8 million for outreach efforts, $28.7 million for development, and $17.2 million for economy-related initiatives. Spending reached its highest levels in April and May before gradually declining in the following months. The Polkadot Treasury balance at the end of Q4 2024 was $168 million.
SupplyPolkadot’s native token DOT serves three primary purposes: governance, staking, and accessing blockspace. DOT has an inflationary monetary policy and no maximum supply. Its monetary policy adjusts according to network conditions, increasing staking rewards when the staked amount falls below the ideal rate to prevent security compromises, and decreasing rewards when the rate is exceeded to maintain liquidity.
In July 2023, Polkadot introduced a new burning mechanism for revenues from its coretime model, following community consensus. This change directs all coretime revenues to be burned, while maintaining a steady treasury inflow through a guaranteed portion of the inflation rate. Specifically, the treasury now receives at least 20% of annual inflation if the ideal staking rate (60%) is achieved, leading to a decrease in staking rewards from 16.67% to 13.33%. The community also voted for a decrease in inflation to further reduce the maximum inflation rate from 10% to 8% in the first year, then further gradually decreasing, which could bring staking rewards down to 10.67% under similar conditions.
Burning coretime revenues marks the second burning mechanism within Polkadot, alongside the existing practice of burning 1% of treasury funds monthly. While the initial impact of coretime burning will be small due to existing lease commitments expiring in 2026, it is expected to gradually grow over time.
As of Q4 2024, Polkadot’s supply metrics included a circulating supply of 1.5 billion (+7.3% QoQ) and a staked supply of 782 million DOT, resulting in 51% of the eligible supply being staked (+13.4% QoQ).
Network Analysis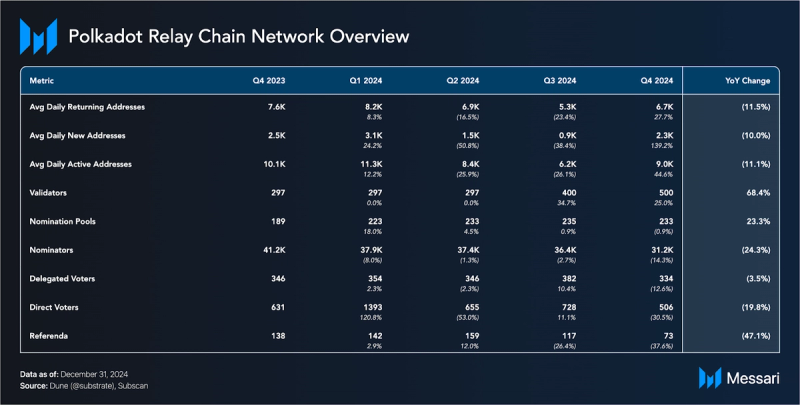 Usage
Usage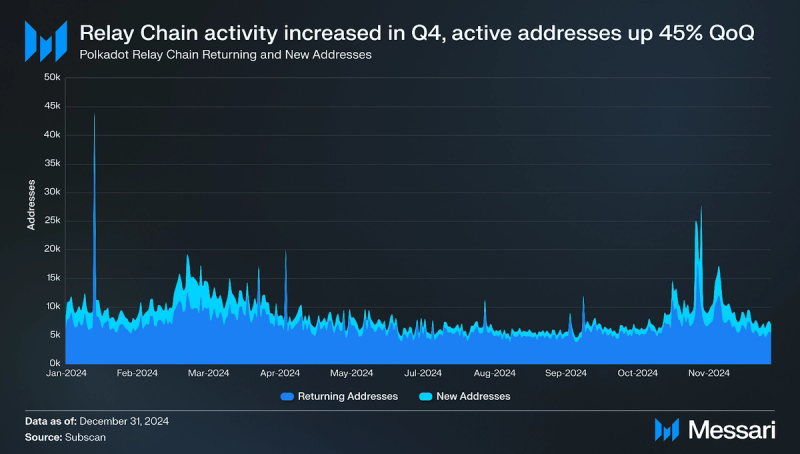
The central Polkadot Chain (aka Relay Chain) has several primary functions, including securing and connecting rollups. Consequently, end users typically transact and use the network primarily through the rollups. The Polkadot Chain does support some end-user functionalities, including token transfers, staking, validator elections, and governance voting. With RFC-0032: Minimal Relay, it is proposed to migrate several of these subsystems into system rollups.
Polkadot Chain activity increased in Q4 2024. Daily active addresses increased to 9,000 (+45% QoQ), daily returning addresses increased to 6,700 (+28% QoQ), and daily new addresses increased to 2,300 (+139% QoQ).
Security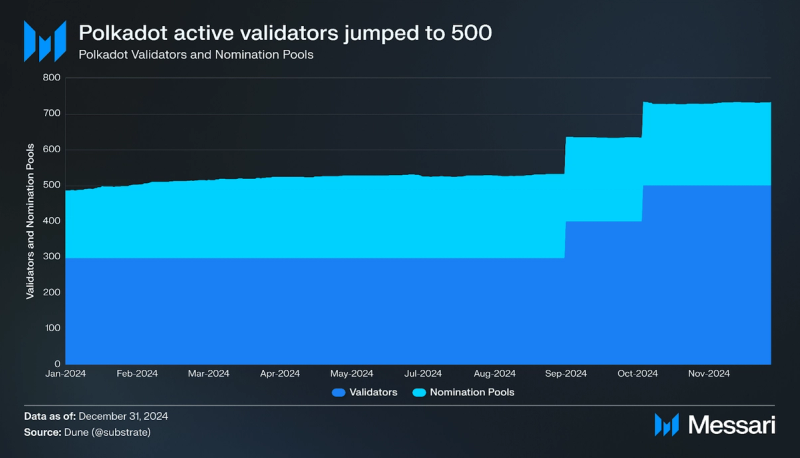
Polkadot uses a Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) model designed to decentralize the validator set. Validators receive payments every 24 hours based on their completion of payable actions known as era points. This model incentivizes nominators to stake with lower-staked validators to earn higher rewards, resulting in a consistently decentralized validator set. The number of active validators increased to 500 due to referendum 888, which enables two approval voting protocol improvements.
The Web3 Foundation launched the Decentralized Nodes Program in October 2024 to support validators. Validators can apply for up to two nodes per network, selected based on technical expertise, reliability, and ecosystem engagement. Selected participants serve a four-month term starting in November 2024, with potential renewal.
As of Q4 2024, there were 31,200 nominators (-14% QoQ). Nomination Pools, which allow users to pool their DOT tokens together on-chain to nominate validators and receive rewards, numbered 233 at the end of Q4 2024 (-1% QoQ).
Governance
OpenGov, the new governance model for Polkadot, has transformed the referendum lifecycle and decentralized the decision-making process. The system allows multiple referenda to run concurrently, enabling faster decision-making. The Council and Technical Committee have been replaced by the Fellowship, a developer DAO that ensures decentralization through community voting, checks and balances, and flexible delegation based on conviction and token commitment.
Governance participation increased substantially in 2024. Referenda submissions rose by 150% and voter turnout by 40% compared to 2023. One of the most significant governance actions of the quarter was Referendum 1200, which increased the active validator set size from 400 to 500. This change passed with 99.7% of votes in favor (1.2 million DOT). Another notable referendum included Referendum 1271, which set Polkadot inflation to 120 million DOT per year. The proposal aimed to provide a more predictable and sustainable economic model for the network. The community's ability to make such economic decisions shows the decentralized nature of Polkadot's governance model.
The SpammeningA recent report on Polkadot’s Kusama network provides insights into its scalability and stability through a large-scale stress test called The Spammening. This experiment took place between November and December 2024 and examined the network's performance under extreme transaction loads in real-world conditions. The results showed that Polkadot reached a peak throughput of 143,343 transactions per second (TPS) while using only 23% of available computing resources. If all 100 cores were utilized, the network’s theoretical throughput could exceed 623,000 TPS.
The test included two approaches. Parity Technologies conducted a network-wide stress test, while a separate community-driven test involved participants manually generating transactions. Both tests ran on live networks with active economic activity, providing a practical view of Polkadot’s capabilities. The experiment applied Polkadot 2.0 features such as Asynchronous Backing, Agile Coretime, and Elastic Scaling. These upgrades improved transaction throughput and resource management. The network maintained stable block times of around six seconds, and finality remained consistent at approximately 16 seconds.
A comparison with other blockchain networks showed Polkadot’s technical advantages. Kusama handled more transactions per second than networks like Solana and Aptos, even with limited resources. These results show that Polkadot can support high-demand applications DeFi and gaming. The report also examines the complexity of measuring performance within Polkadot’s multichain architecture. Instead of relying on traditional TPS metrics, it suggests using aggregate throughput and validator efficiency for a clearer assessment.
Future plans include additional tests to further analyze performance and scalability under different conditions. Upcoming stress tests will take place on Polkadot’s main network, where higher node capacity and stronger connectivity could lead to better results. These efforts build on current findings and set new benchmarks for blockchain performance in real-world environments.
RoadmapPolkadot's core technology evolved in Q4 2024 with advancements that improved current capabilities and laid the groundwork for Polkadot 2.0. The quarter saw improvements intended to increase network efficiency and reduce entry barriers for developers. Asynchronous Backing and Agile Coretime were fully implemented and contributed to the surge in transaction volumes across parachains. The final piece of the Polkadot 2.0 architecture, Elastic Scaling, is due to go live before the end of Q1 2025.
Building on these improvements, Polkadot focused on further technological advancements:
- JAM Technology Development: On November 11, Gavin Wood shared insights into Polkadot's JAM (JOIN-ACCUMULATE MACHINE) technology through a global tour of lectures, presentations, and blog posts. This signaled a push for broader understanding within the ecosystem. On November 29, Parity Technologies released the Polkadot JAM Rust SDK. This provides developers with tools to build on the network using JAM technology. This release supports the developer community and supports progress within the ecosystem.
- Developer Tools and SDKs: The introduction of the Polkadot Unity SDK for Gaming by Ajuna Network empowers game developers to integrate blockchain into their projects. Unity powers over 50% of the top 1,000 mobile games worldwide, positioning this SDK as a potential driver for Web3 gaming adoption. Additionally, new APIs, including the XCMFee Payment Runtime API and XCMDryRunApi, were introduced to improve cross-chain efficiency.
- Roadmap to Polkadot 2.0: Developments in Q4 2024 aligned with the broader goal of fully implementing Polkadot 2.0 in 2025. Gavin Wood emphasized horizontal scaling as the preferred approach, which aligns with Polkadot's decentralized nature. The roadmap includes the concept of a JAM Grid, designed at creating a decentralized Web3 supercomputer, alongside rebranding efforts to simplify user interactions.
- The focus of engineering collective Parity Technologies, the main technical contributor to Polkadot, is the launch of Ethereum-compatible smart contracts, native to Polkadot, amid widespread improvements to the existing developer experience, including lower barriers of entry, ultra-low costs, and easier access to stablecoins.
Polkadot's technical development continues with efforts to expand transaction capacity, provide better tools for developers, and optimize network operations. As Polkadot 2.0 nears, these changes are expected to increase system performance and compatibility across the ecosystem.
For a deep dive on Polkadot 2.0, check out our report Polkadot 2.0 Rebirth: An Overview.
Closing SummaryPolkadot experienced a surge in transaction volume and technical progress in Q4 2024. Monthly transactions climbed to 60 million by November, with Neuroweb and Frequency in the lead. Agile Coretime introduced a dynamic resource allocation system, which optimizes scalability to meet demand fluctuations. With the launch of Snowbridge, a trustless Polkadot-Ethereum Bridge, and other cross-chain solutions like Hyperbridge, asset transfers became more efficient and reliable.
By December, DOT’s market capitalization had grown 71% QoQ, reaching $16.4 billion at its peak. Transaction fees followed suit, increasing in response to greater network activity. Treasury spending supported outreach and development by channeling resources into initiatives that expanded the ecosystem. OpenGov restructured governance, which helped streamline decision-making and encouraged broader community involvement. Looking ahead, Polkadot plans to complete the transition to Polkadot 2.0, paving the way for the introduction of radical new technologies like JAM, which involves a complete replacement of the Polkadot Chain (aka Relay Chain).
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright 2025, Central Coast Communications, Inc.