and the distribution of digital products.
DM Television
Understanding Quai Network: A Comprehensive Overview
- The novel Proof of Entropy Minama (PoEM) consensus mechanism increases PoW blockchain finality guarantees. These new guarantees enable Quai Network to theoretically achieve 50,000 TPS and improve confirmation delay by approximately 40%.
- A dual ledger system enables the creation of QUAI and QI, which have inherently different properties dependent on the ledger on which they live. QUAI lives on the account-based ledger, while QI lives on the UTXO-based ledger.
- QI is the first flatcoin to be backed by the global mining market. The issuance of QI is directly proportional to the network’s hash rate, which, in the long run, is dependent on the electricity available to the network.
- Merged mining combined with PoEM enables cross-chain communication, allowing a sharded blockchain network to have properties similar to those of a monolithic blockchain.
Quai Network is a multi-threaded, merged mined, Proof-of-Work (PoW), sharded blockchain secured by its novel consensus mechanism Proof-of-Entropy-Minima (PoEM). Furthermore, Quai Network introduces a dual cryptocurrency and ledger system with QUAI and QI. QUAI is on the account-based ledger and functions principally as the store of value for the network. Meanwhile, QI is on the unspent transaction output (UTXO) based ledger and functions more as digital cash.
Miners are rewarded in either QUAI or QI, depending on their preference at the time, with both QUAI and QI’s issuance being a function of network difficulty. QUAI is issued based on the logarithm of network difficulty, while QI is issued at a rate directly proportional to the network’s difficulty. Quai Network’s difficulty is dependent on the hash power made available to the network via miners. Miner's costs, in the long run, boil down to the electricity they use to mine blocks for Quai Network. In this way, miners who elect to receive mining rewards in QI are converting energy into QI. This ties QI directly to the miner's input costs in the long run, making it the first decentralized flatcoin tied to energy through mining. A flatcoin is designed to maintain purchasing power over time, and in QI’s case, it is designed to maintain the purchasing power of the units of energy used to mine it.
Copilot Insights: Flatcoins vs StablecoinsQuai Network's hierarchical multichain design is interlinked and secured through merged mining, allowing it to scale dynamically to match the throughput needed. This design offers a solution to the multichain interoperability problem plaguing today's multichain structures.
BackgroundThe idea for Quai began in 2018 while Karl Kreder, who would later cofound Quai Network, was working at the hardware wallet startup he had cofounded, GridPlus. This idea would later become a paper discussing the initial premise of a PoW blockchain hierarchy and securing it through merged mining. Later, Dr. Kreder brought this idea to Sriram Vishwanath, an Electrical and Computer Engineering professor at The University of Texas at Austin. Dr. Vishwanath gathered some graduate students, including Alan Orwick, to further explore the idea after they had received a grant from the National Science Foundation in 2019. After some time, the group published their research on scaling PoW blockchains through a hierarchy of merged mined blockchains initially called BlockReduce. During this time period, the group successfully launched Quai Network’s Stone Age and Bronze Age testnets. These testnets showcased the initial potential of the Quai Network with the Bronze Age testnet, resulting in over 1.5 million blocks, 100,000 transactions, and 1,700 nodes across the globe. Subsequently, Orwick pitched the idea to Polychain Capital in 2022, which led to their investment of $8 million into Quai Network, allowing the team to focus full-time on building Quai Network. A few months later in 2022, Quai Network would raise $2 million from Alumni Ventures, and in 2024, they raised $5 million in a strategic round.
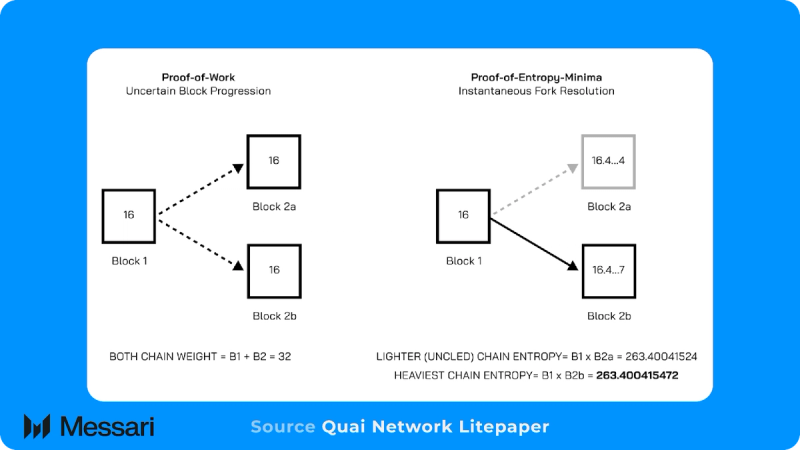
TechnologyProof of Entropy Minama (PoEM)Proof of Entropy Minama (PoEM) is a novel PoW consensus algorithm that builds upon Bitcoin’s consensus to decrease confirmation times and increase throughput. Bitcoin relies on the heaviest chain rule (HCR), which determines the canonical chain of blocks by summing the cumulative difficulty of the blocks. PoEM builds upon the HCR by summing the cumulative difficulty of the blocks while taking into account the entirety of the proposed block hash. This consideration of the entirety of the proposed block hash allows for faster fork resolution.

The first step in determining if a Bitcoin block is valid is determining if it hit the correct difficulty threshold. The difficulty threshold determines the minimum number of leading zeros a block hash must contain to produce a valid block. Occasionally, two miners will mine a valid block around the same time as each other and forward the block hash to Bitcoin nodes. During this time, the Bitcoin miners will split it into two groups. One group will mine on block A, and the other will mine on block B. The group that comes up with the next block first will extend the chain in their block’s direction, and the other block will be orphaned. In this scenario, effectively half of the network is wasting its hashpower on looking for a hash for a block that will be orphaned and not added to the Bitcoin blockchain. PoEM addresses this by ensuring that the difficulty threshold is met while also comparing the rest of the block's proposed hash to determine which one should be added to the blockchain, improving confirmation delay by approximately 40%.
PoEM’s novel consensus architecture allows for significantly faster blockchain finality and drastically less uncertainty regarding the last block, or chain tip, for PoW blockchains. This increased certainty of the last block of the blockchain, the tip, enables multi-blockchain communication through merged mining.
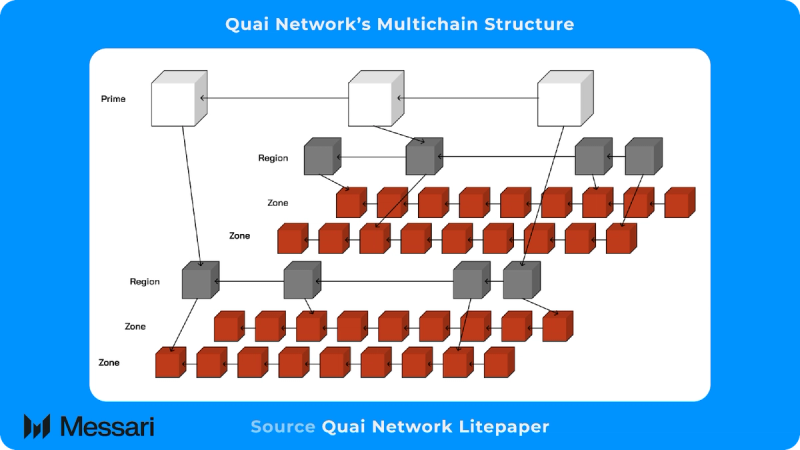
 Multichain structure
Multichain structureQuai Network is a congregation of interlinked blockchains with a hierarchical structure. There are three levels in this hierarchy:
- Zone: This is the lowest level of the hierarchical structure. Each Zone blockchain maintains its own state, where the user's transactions are executed. Zone blockchains are linked to a dominant Region blockchain through merged mining.
- Region: This is the middle level of the hierarchical structure. Zone blockchains use this level to communicate with other Zone blockchains in the same Region. They also forward inter-region transactions to the Prime blockchain. Region blockchains do not carry state or execute transactions. They exist solely to communicate between Zone blockchains.
- Prime: This is the highest level of the hierarchical structure. The Prime blockchain does not carry state or execute transactions. It exists solely to communicate between Region blockchains.
Quai Network leverages sharding to automatically scale to meet network demand and increase the overall throughput of the network. In the case of Quai Network, shards are zone blockchains and allow for separate execution and state environments. When the network’s uncle rate reaches a certain threshold for a specific amount of time, the protocol will trigger the creation of a new shard, which may also require the creation of a new region blockchain. Uncle blocks are valid blocks that were proposed close to the time the canonical block was proposed. PoEM ensures that the canonical block is quickly chosen, but uncle blocks, in aggregate, result in wasted hashpower.
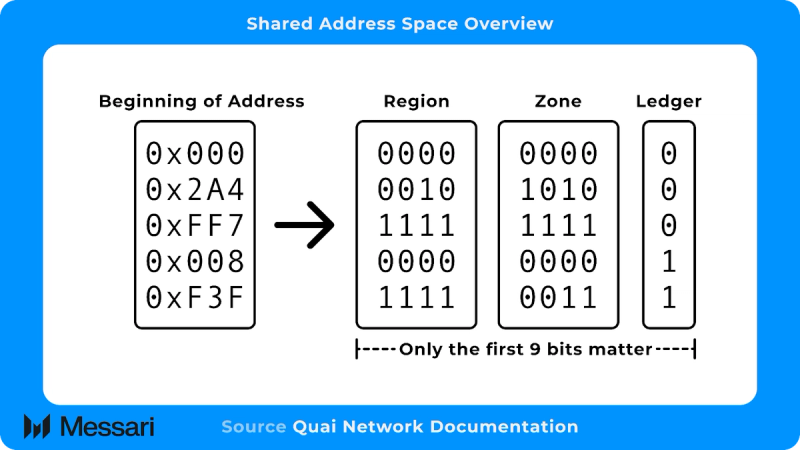
Quai Network uses differences in address space to allow nodes and wallets to quickly identify which zone, region, and ledger is affected. This is done by decoding the first 9 bits of an address.
- Bits 0-3 identify the Region.
- Bits 4-7 identify the Zone.
- Bit 8 identifies the address's ledger.
- The account-based ledger is represented by 0.
- The UTXO-based ledger is represented by 1.
For example, an address starting with 0x000 would live in Region 1, Zone 1, and on the account-based ledger. However, an address starting with 0x008 would also live in Region 1 and Zone 1, but instead of using the account-based ledger, it would use the UTXO ledger, denoted by the 9th bit being 1.
Merged MiningMerged mining allows miners to mine multiple blockchains simultaneously as long as they use the same hashing algorithm. Each blockchain in the hierarchical structure of Quai Network uses the same Programmatic PoW (ProgPoW) hashing algorithm, which enables merged mining to be leveraged. ProgPoW is an Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) resistant hashing algorithm that favors miners to mine using GPUs, which are more widely available than ASICs. Having a mining algorithm that favors GPUs also makes it more accessible, allowing a wider set of participants to be involved in securing the network.
When mining for Quai Network, miners must merge mine the prime blockchain, a region blockchain, and a zone blockchain. This represents the smallest subsection of the network that can be run trustlessly. Each hierarchical layer of the network has a different difficulty level, the highest being prime blocks and the lowest for zone blocks. The increased difficulty associated with each level also means that each level will take a different amount of time to add blocks to its respective blockchains. Since prime blocks are the most difficult, they take the longest to find, but once they are found, they satisfy the requirements for all three blockchains. However, miners may only find a valid zone block while mining, which means the block would only be added to the zone blockchain. Merged mining requires no additional hardware or energy to function and helps increase the throughput of the entire network. This is achieved through asynchronous blockchain extension, while occasional coincidence blocks tie the network together by satisfying the requirements of all three blockchain levels. Additionally, merged mining in conjunction with PoEM powers Quai Network’s cross-chain communication abilities, increasing throughput to new levels for a PoW blockchain.
Execution LayerQuai Network uses the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to power its smart contract platform. Each zone blockchain in the Quai Network functions as its own EVM layer with a unique state history. State history in this context would be the balance changes for all accounts and smart contracts, along with all the code and storage associated with smart contracts. However, state growth can become a problem over time if not appropriately managed. Quai Network will address this issue by charging state rent priced logarithmically based on the size of the state. This passes the cost of increasing the state of the network to the individuals who are directly increasing it.
Copilot Insights: What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine?Quai Network incorporates EVM transaction parallelization within each zone blockchain, allowing for increased throughput. This is accomplished via the use of enforced access lists. Traditionally, EVM-based blockchains execute transactions one at a time, analogous to a single thread on a CPU. This is to avoid multiple transactions affecting the same accounts or storage slots. The reason this can even occur in the first place is that the accounts and/or storage slots a transaction interacts with are not known until the transaction is actually executed. To avoid this, Quai Network requires transactions to declare an access list of what accounts and/or storage slots the transaction will interact with. This allows Quai to execute transactions in parallel as long as no overlapping elements exist in their respective access lists. This method of transaction parallelization is built on the fact that most EVM transactions do not overlap, allowing them to be executed simultaneously.
TokenomicsDual Token and Ledger DesignQuai Network operates under a dual token and ledger architecture, enabling it to serve a wider variety of use cases. The QUAI token lives on an account-based ledger, and QI lives on a UTXO-based ledger. Ethereum popularized the account-based ledger, which resembles the traditional banking system. In this system, transactions are credits or debits of an account that can be summed to get an account's balance. Bitcoin popularized the UTXO-based ledger and resembles cash. In this system, the denominations and amounts of an asset being transferred are what matters, with a wallet's balance being the sum of the different denominations of cryptocurrency it holds. This dual token and ledger system affords users more privacy than they otherwise would if they were limited to one or another ledger. QUAI and QI are both issued as miner rewards, with miners selecting which token they wish to receive. Miners can change the token that they are rewarded in on a per-block basis. Each of them serves as the native token on their respective ledgers.
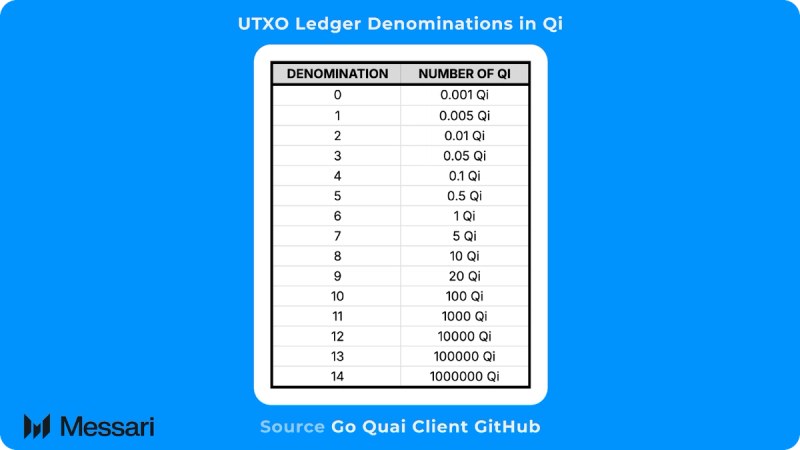
QI lives on the UTXO ledger and enables users to transact and transfer value as they would with cash. The UTXO ledger is broken down into 14 unique denominations, which correspond to 14 different units of QI. Additionally, Quai Network will prohibit the reuse of addresses at least per block for QI transactions to increase privacy. The prohibiting of address reuse and a small set of fixed denominations allow users to transact more privately than they otherwise would be able to. This is because every denomination of QI is fungible, and transfers of QI are fundamentally tied to the denominations of QI transferred.
Meanwhile, QUAI, unlike QI, lives on the EVM compactable portion of the blockchain, allowing users to interact with smart contracts in the same way they would on any other EVM-based blockchain. This enables QUAI to be the value transfer vehicle of the programmable monetary layer, while QI is the backbone of the privacy-centric monetary layer.
Rewards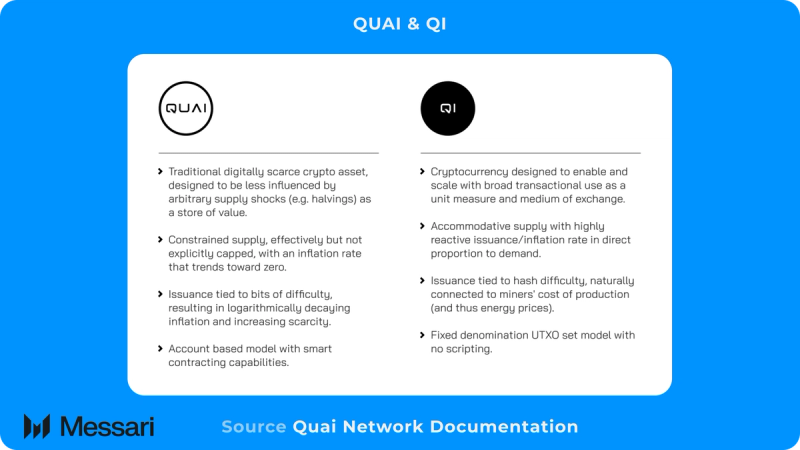
Quai Network miners can choose which cryptocurrency they want to be rewarded in, QUAI (pronounced “k-why”) or QI (pronounced “chee”). Each has a different issuance schedule designed to provide unique monetary properties to each coin. Additionally, miners are able to lock their rewards for a variable amount of time to earn an increased amount of QUAI or QI. This time-based reward lock also serves to help protect the network from malicious miners as it creates a sunk cost that miners would stand to lose if they were to try and attack the blockchain. The available lockup durations and multiples will be announced before the mainnet launch.
Additionally, miner rewards are smoothed by getting rewarded based on their work in mining blocks through a concept called workshares. While mining, miners occasionally propagate a workshare to their peers, relaying information about the block and transactions known to them. This effectively creates a distributed mining pool protocol directly into the base protocol and allows solo miners to get paid 20-50 times as often as they would without it.
Copilot Insights: What are workshares?QI is issued at a rate directly proportional to the amount of work a miner exerted to mine a block. In essence, the higher the difficulty, the more QI will reward the miner. The network's difficulty is directly tied to the overall hash rate available at a given moment in time, with the hash rate, in turn, being the product of GPUs and electricity. Through this supply chain, QI becomes the commoditized output of these inputs, effectively deriving its value from the value of electricity in the long run and becoming a flatcoin. Unlike stablecoins, flatcoins aim to maintain purchasing power over time, and in QI’s case, it aims to retain the purchasing power of the energy used to mine it.
The dual currency design for Quai Network was heavily influenced by Gresham's Law, which states that an inferior form of money will drive out a better form of money from circulation. This is due to the fact that a superior form of money acts as a store of value, which makes people want to keep it, while an inferior form of money has a lower future expected value, which is why it should be spent now rather than in the future. In this way, QI serves as the inferior currency because it is tied to global energy production, which should increase in the long run. QUAI serves as the store of value within the dual monetary system that Quai Network employs. QUAI is issued proportionately to the logarithmic difficulty level, which means that less QUAI will be issued over time. This will ultimately cause it to trend to a finite supply like BTC.
Quai Network will have a native conversion mechanism allowing anyone to swap QUAI for QI or vice versa. The mechanism, developed in collaboration with BlockScience, creates a dynamic market-based exchange rate between Qi and Quai. The controller is designed under the following assumptions:
- Firstly, miners will only elect to receive rewards in QI when QI is above their production costs.
- The second idea is that the controller offers a neutral rate to the market, meaning that the miners and market participants roughly want to convert QUAI to QI and QI to QUAI proportionally to each other.
When doing a conversion, it will be locked up for two weeks. The exact design of the mechanism to accomplish this is still being finalized. Nevertheless, the controller ultimately creates a fluid interlink between QUAI and QI, ensuring that the Quai Network has all three properties of money with both a superior and inferior form of it.
Genesis QUAI Distribution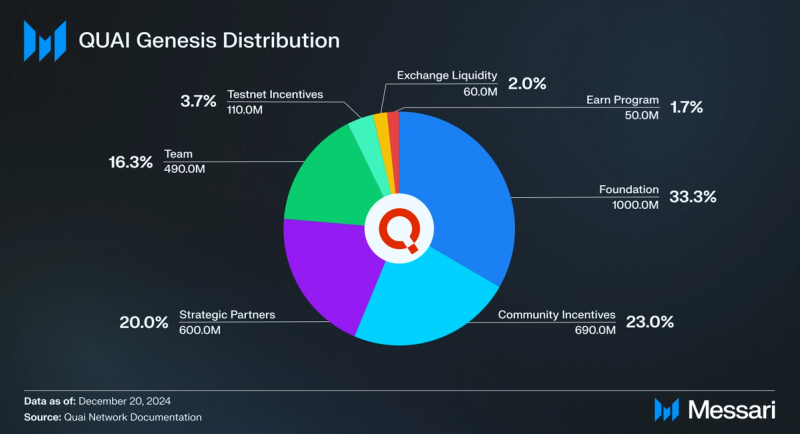
The Quai Network genesis block will create 3 billion QUAI and distribute it to the following stakeholders.
- Foundation (33.3%): Driving adoption of Quai Network while securing resources for future needs and safeguarding the project's adaptability, regardless of market conditions.
- Community Incentives (23.0%): Empowering community participation by offering predefined and fair rewards that drive meaningful contributions and foster a vibrant ecosystem.
- Strategic Partners (20.0%): Building alliances with key entities to unlock access to capital, technology, and expertise to accelerate innovation and growth.
- Team (16.3%): Ensuring long-term commitment by attracting, retaining, and aligning the team's incentives with the project’s success and fostering their sustained investment in its future.
- Testnet Incentives (3.7%): Strengthening the network by incentivizing community-driven testing and optimization, ensuring a seamless and robust deployment.
- Exchange Liquidity (2.0%): Enhancing token accessibility and fair pricing through sufficient liquidity, promoting investor confidence and user engagement.
- Earn Program (1.7%): Encouraging network-supporting activities to reinforce decentralization and drive active participation.
Quai Network has steadily progressed through four testnets—Stone Age, Bronze Age, Iron Age, and Golden Age—each designed to refine its PoW multichain blockchain architecture and demonstrate its capabilities. The Stone Age Testnet (November 17, 2021 – December 15, 2021) served as the network’s foundational phase, laying the groundwork for subsequent advancements. Building on this, the Bronze Age Testnet (February 18, 2022 – March 23, 2022) marked significant milestones with 1,700 active nodes, 1.4 million blocks mined, over 110,000 transactions, and contributions from 1,070 unique miners using 2,089 mining addresses. This testnet not only improved core protocol features but also tested essential tools such as stats pages, explorers, faucets, and wallets, all of which remained in their alpha stages. Moreover, the Bronze Age demonstrated Quai’s global reach and decentralized structure, with participation from across the globe and transaction throughput surging toward the end of the testnet, driven by reduced propagation delays and the successful launch of the faucet.
The Iron Age Testnet (September 19, 2023 – March 12, 2024) represented a significant leap forward, introducing live EVMs on each of its nine shards, GPU mining, and the implementation of PoEM consensus. The testnet achieved impressive milestones, peaking at over 2,000 TPS and 120 gigahash per second (GH/s). Structured into four phases, the Iron Age began with securing the network through node and miner support, progressively scaling TPS limits from 450 to 1,800. It transitioned into integrating decentralized applications and smart contracts, onboarding users with marketing campaigns and incentives, and finally testing deployed dapps. These phases culminated in a robust, scalable environment that prepared the network for its next phase.
The Golden Age Testnet (October 15, 2024 – January 8, 2025) is the most advanced and feature-complete testnet to date. The testnet has produced over 1.3 million blocks containing over 22.4 million transactions and had an average block time of 5.0 seconds with over 47,000 unique wallet addresses participating in the testnet. During the month of December, the network was secured by GPU miners to the tune of roughly 375 GH/s. The last core building block of the network will be the implementation and testing of the QUAI/QI controller. The Golden Age testnet will conclude by validating and refining the QUAI/QI controller mechanism design, using a hard fork, mining behavior analysis, and tuning adjustments to ensure optimal performance. This final phase marks a critical step toward Quai Network’s highly anticipated mainnet launch in January 2025.
EcosystemThe Quai Network ecosystem has become home to a diverse range of projects and applications that leverage its multichain architecture to deliver innovative solutions across various domains.
DeFiThe QuaiSwap DEX enables users to add liquidity for their favorite tokens and swap between them. IceCream Swap serves as an AI-powered DEX aggregator, allowing users to trade tokens at optimal rates while offering DeFi utilities such as bridging and a launchpad. In the realm of decentralized finance, Blueberry protocol enables lending and leveraged borrowing up to 20x collateral value, with integrated strategies such as yield arbitraging and automated vaults. For those seeking a secure and efficient path to Bitcoin, Portal Finance offers a custody-less cross-chain solution, while Lumerin facilitates decentralized trading of Bitcoin hashpower.
NFTs & GamingQuaiMark provides a platform for buying, selling, and exploring digital assets, with Quai Faces, Quai Miners, and Diverse Beauty showcasing unique NFT collections that highlight creativity and diversity. Additionally, Quai Penguins offers a vibrant NFT project focused on avatar integration and ecosystem expansion.
On the gaming front, Quai Battle is a multiplayer game where players compete to collect coins, grow stronger, and dominate the leaderboard. Meanwhile, QFan, a GameFi dApp on Telegram, combines Play-to-Earn and Predict-to-Earn mechanics with event hosting and marketing features, creating a dynamic and engaging experience.
Quai Network’s GPU powered mining architecture positions it to be an alternative outlet for decentralized AI and compute depending on the demand for those services. Quai Network and io.net have a partnership that helps facilitate the scaling of Quai Network from its testnet phase to mainnet by integrating io.net’s decentralized computing network. Additionally, Quai Network recently integrated with Akash Network’s decentralized compute marketplace, enabling miners to access decentralized operations through Akash nodes.
Wallets & InfrastructureThe Quai explorer serves as home base for Quai Network’s blocks, transactions, and accounts. Stork Network brings utility to developers by providing decentralized, reliable, and unique data solutions via its oracle network. Mining pools like AlphaPool and LuckyPool allow miners to pool their GPU power and mine collectively.
Pelagus Wallet is an open-source wallet designed specifically for Quai's architecture. It simplifies multichain account management, smart contract interactions, and asset storage for users with features like smart transaction routing. Wallet solutions are integral to the ecosystem; the more of them, the better. Koala Wallet delivers a seamless self-custody experience with multichain compatibility.
Together, these projects scratch the surface of what is possible while catering to a broad spectrum of use cases and user needs.
Closing SummaryQuai Network represents the culmination of years of work to design proper technical and economic mechanisms to create a scalable, decentralized, and secure blockchain. This is principally possible because of the innovations to blockchain consensus by PoEM. Creating such a high level of certainty of the tip of a blockchain, combined with merged mining, provides for the finality guarantees needed to enable cross-chain communication. In turn, this allows for a network of sharded blockchains to work tangentially, increasing throughput to new levels never for a PoW blockchain.
Furthermore, Quai Network creates the first flatcoin tied to energy in QI, representing the most natural and ubiquitous pricing input for goods. Additionally, QI lives on a UTXO ledger, giving it cash-like properties, while QUAI functions as the store of value that will be the backbone of the EVM smart contract network. Finally, the QUAI ↔ QI controller will be the bridge that connects the two cryptocurrencies to create a monetary link that will be able to serve every user’s transactional needs. With all of its innovation, Quai Network is attempting to showcase what a next generation PoW blockchain can achieve.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.