and the distribution of digital products.
The Mathematical Formula to Hyperinflation
:::info Author:
(1) Laurence Francis Lacey, Lacey Solutions Ltd, Skerries, County Dublin, Ireland.
:::
:::tip Editor's Note: This is Part 4 of 7 of a study on how changes in the money supply, economic growth, and savings levels affect inflation. Read the rest below.
:::
Table of Links- Abstract and 1 Introduction
- 2. Methods
- 2.1 Statistical Methodology
- 2.2 US Time Series Data
- 2.3 Hyperinflation Model
- 3. Results
- 3.1 Characterisation of Price Inflation
- 3.2 Characterisation of Hyperinflation in the Weimar Republic (1922 to 1923)
- 4. Discussion
- 5. Conclusion, Supplementary materials, Acknowledgements, and References
- AppendixLaurence Francis Lacey
- \
A mathematical statistical characterisation of a hyperinflation process is given in the Supplementary Appendix, building on the original characterisation of a process with a monoexponentially increasing sample space [5]. As is shown in the Supplementary Appendix, an exponential growth process becomes a double exponential growth process, when a second exponential growth process occurs, at some point in time (t*), on top of the initial exponential growth process.
\ When t < t*,
\
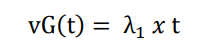
\ When t ≥ t*,
\
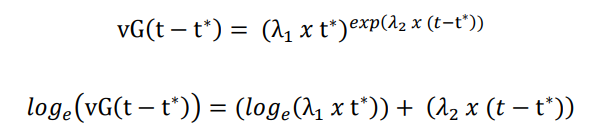
\ While the information entropy of an expansionary process can be considered to be related to the “velocity” of the expansion, the natural log of the information entropy of an expansionary process can be considered to be related to the “acceleration” of the expansion.
\ The double exponential nature of some cases of monetary hyperinflation has been investigated [13] and there has been an exploratory investigation of a double exponential hyperinflationary process, using the information entropy methodology [6].
\ All plots of the data analysis given below were obtained using Microsoft Excel 2019, 32- bit version.
\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.