and the distribution of digital products.
DM Television
How BayesPPDSurv Brings Cutting-Edge Bayesian Survival Modeling to the Masses
:::info Authors:
(1) Yueqi Shen, Department of Biostatistics, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill ([email protected]);
(2) Matthew A. Psioda, GSK;
(3) Joseph G. Ibrahim, Department of Biostatistics, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
:::
Table of LinksAbstract and 1 Introduction: BayesPPDSurv
2 Theoretical Framework
2.1 The Power Prior and the Normalized Power Prior
2.2 The Piecewise Constant Hazard Proportional Hazards (PWCH-PH) Model
2.3 Power Prior for the PWCH-PH Model
2.4 Implementing the Normalized Power Prior for the PWCH-PH Model
2.5 Bayesian Sample Size Determination
2.6 Data Simulation for the PWCH-PH Model
4 Case Study: Melanoma Clinical Trial Design
2 Theoretical Framework 2.1 The Power Prior and the Normalized Power Prior
\
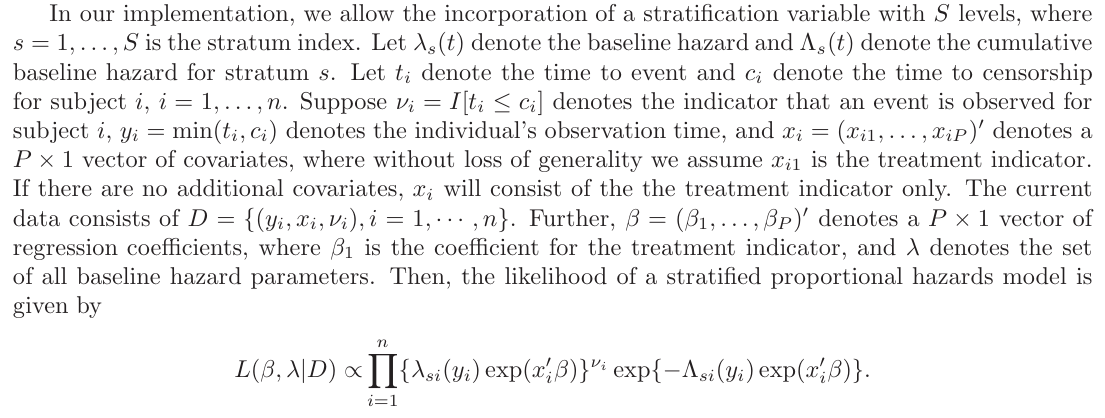
2.2 The Piecewise Constant Hazard Proportional Hazards (PWCH-PH) ModelIn BayesPPDSurv, we implement the stratified proportional hazards model with piecewise constant baseline hazard within each stratum, which is a common approach for Bayesian analysis of time-to-event data (Ibrahim et al., 2001). \n
\
\
\

\
2.3 Power Prior for the PWCH-PH Model\
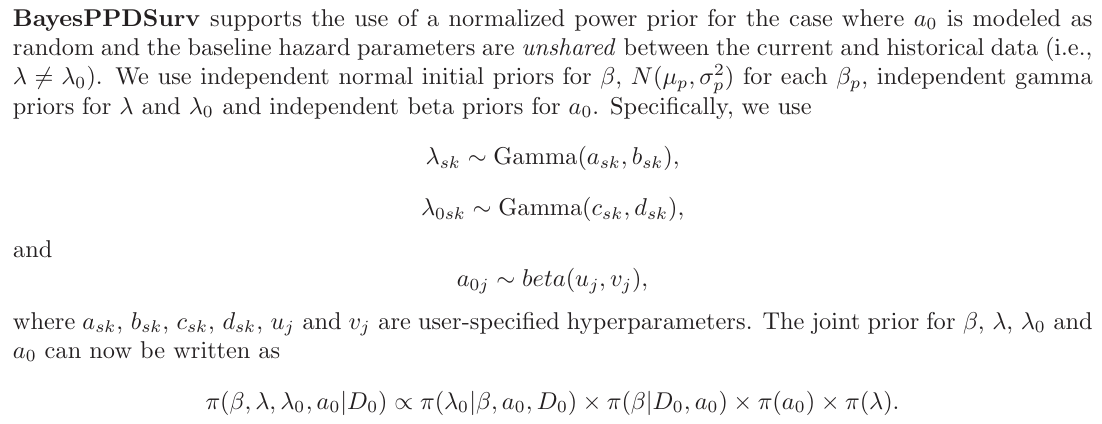
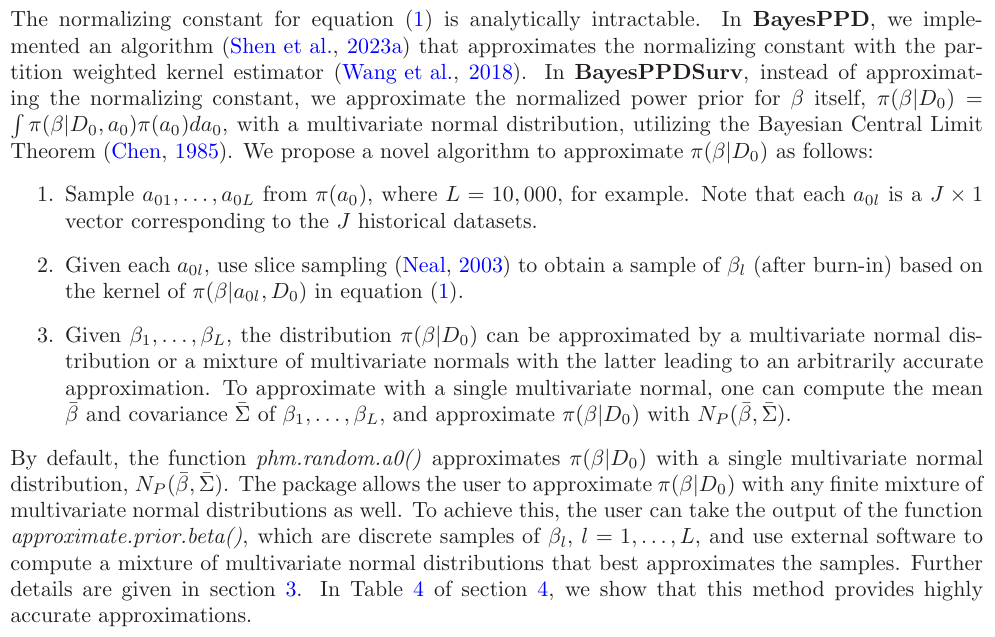
 \n 2.4 Implementing the Normalized Power Prior for the PWCH-PH Model
\n 2.4 Implementing the Normalized Power Prior for the PWCH-PH Model
\
\
\
\

\
\
\
\
2.5 Bayesian Sample Size Determination\

\
2.6 Data Simulation for the PWCH-PH ModelFollowing Psioda et al. (2018), we describe the steps for simulating the observed data for the PWCHPH model. We simulate the complete data for subject i through the following procedure:
\
\

\ \ The above procedure yields a hypothetical complete dataset corresponding to a scenario where all subjects are followed until the event is observed or they drop out. One constructs the observed dataset from the complete dataset as follows:
\
\

\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed (Attribution 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.