and the distribution of digital products.
Building Scalable Event-Driven Orchestration Platform in AWS
These days, we’re surrounded by apps everywhere—on our phones, in our smart homes, and throughout businesses big and small. It’s almost unbelievable how much data they churn out every single day. We're talking billions or trillions of events, from a simple tap on a phone screen to complex business transactions. It is essential for applications to handle these events in real-time to act on them as they occur and derive useful insights for the growth of the business.
\ Now, imagine if we could tap into all this information as it happens, in real-time. That's where the magic of event-driven architecture comes in. It's like having a super-efficient personal assistant for the application, one that is always on the job and can handle a huge number of tasks.
Sample Applications of Event-Driven ArchitectureE-Commerce Platforms
Each time an order is placed, it triggers events that are received by multiple services. As the order is confirmed, an event is sent to update inventory, process the payment, order tracking, and send email confirmation. All of these happen instantly and independently from each other.
\
Online Multiplayer Gaming Platforms
Every player's action whether it’s scoring points or making a move creates events that update the game state, update game sources, and keep everyone in the game on the same page.
\
Social Media Platforms
Every action by the user for example liking a post, or following another person or group impacts triggers events. Messages, comments, and other interactions trigger their own events, allowing real-time updates across millions or billions of users.
\ Many other real-world scenarios are suitable as a perfect match for event-driven architecture.
\
Event-Driven Orchestration in AWSHandling such a massive flow of events requires an event orchestration platform that is highly scalable, resilient, and reliable. The platform should scale as the events grow, should handle spikes on the load of events, and deliver the events to each relevant service without fail.
\ AWS provides SNS (Simple Notification Service), SQS (Simple Queue Service), and Lambda to build such an orchestration platform with ease. We can build a sophisticated orchestration platform with these key elements in AWS.
\
- SNS acts as a message publisher, notifying all subscribers when an event occurs. It allows for a fan-out model where multiple endpoints (e.g., SQS queues, Lambda functions) can receive the same message simultaneously.
- SQS can subscribe to SNS and it acts as a durable message queue, buffering requests, and decoupling services. SQS ensures reliable message delivery and provides visibility and dead-letter queues to handle failed messages.
- Lambda handles event processing logic. Each Lambda function is stateless, scaling automatically based on incoming events. It can consume events from SQS queues, process data, and invoke other services as necessary.
\
\
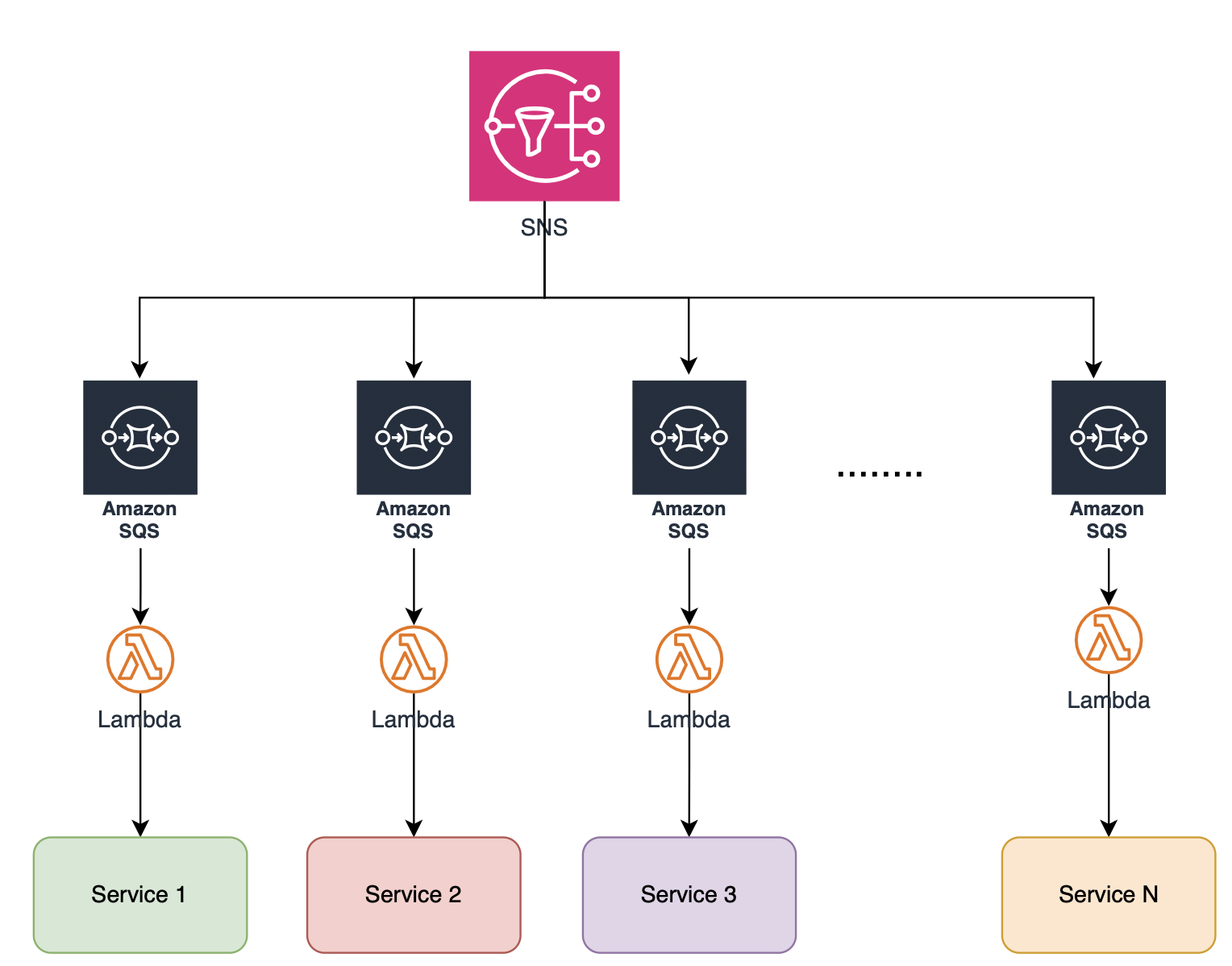
\ \ Note that SNS can deliver events directly to the application service without SQS/Lambda in the flow. There are many advantages of using SQS & Lambda, few of them are:
\
Reliability
SQS gives us the ability to buffer the events if the service is temporarily unavailable or under heavy load
Event Filtering
We can choose which events that SQS can subscribe to
Error Handling
By combining SQS + Lambda, we gain enhanced error-handling capability and retry mechanisms
Event Trigger
A user places an order. This triggers an SNS notification to distribute the event to multiple interested services
Fan-Out
SNS sends the message to various SQS queues (based on the filtering of events). Each queue can belong to a corresponding service - Inventory Service, Payment Processor Service, or Notification Service
Processing
Each SQS queue triggers its respective Lambda function, which sends the event to the corresponding service
\
Monitoring and AlertingEnsuring high availability and reliability for your event-driven applications requires thorough monitoring and alerting
- AWS CloudWatch: Monitors Lambda invocations, SQS queue depth, and SNS message delivery. We can set up CloudWatch Alarms to alert on metrics like
- Lambda duration, errors, and throttling
- SQS queue message delay and age
- SNS delivery success rates
- AWS X-Ray: Allows tracing of Lambda invocations and helps pinpoint latencies or issues in inter-service communications
- AWS CloudTrail: Logs all SNS, SQS, and Lambda actions, providing an audit trail for actions and configurations within your application
\
SLA & ScalingUnderstanding SLAs for each AWS service in the stack ensures the architecture meets uptime and availability requirements.
| Service | SLA | Scale & Key Limitations | |----|----|----| | SNS | 99.9% | Scales automatically; high publish rate of up to tens of millions of messages per second. | | SQS | 99.9% | Allows up to 3000 messages per second per queue; messages retained for up to 14 days. | | Lambda | 99.95% | Automatically scales in response to events; 1000 concurrent executions per account by default (can be increased). |
These SLAs help ensure that your services remain available and resilient to handle high-traffic periods, with each component designed to meet varying throughput and reliability needs.
\
Building the Application Step-By-StepThe Cloudformation templates for orchestration platform is available here. We can go through the important snippets of the templates in the following sections.
\
Create SNS Topic
Define an SNS topic. SNS will handle the fan-out to subscribed queues.
\ \
Setup SQS Queue
For each downstream service, create an SQS queue
\ \
Setup Lambda Functions
Create Lambda functions that will process messages from each SQS queue.
\ \ The rest of the templates to create subscriptions, roles, are available in Github Repo. Use CloudWatch metrics and alarms to track message failures, Lambda duration, errors, and other key metrics.
\
Scaling ConsiderationsThis event-driven platform automatically scales:
- SNS offers high scalability with an inherent upper limit on subscribers or messages.
- SQS supports robust scalability, with very high message throughput per queue.
- Lambda provides automatic scaling that adjusts concurrency based on incoming request rates.
AWS’s event-driven orchestration platform with SNS, SQS, and Lambda allows for a powerful, and flexible approach to build scalable and resilient applications. From e-commerce order processing to data pipelines, this serverless approach enables developers to build powerful, decoupled applications capable of handling complex workflows across multiple services. To ensure observability and maintainability, AWS provides integrated monitoring and debugging tools.
- Home
- About Us
- Write For Us / Submit Content
- Advertising And Affiliates
- Feeds And Syndication
- Contact Us
- Login
- Privacy
All Rights Reserved. Copyright , Central Coast Communications, Inc.